Where Is the Ford Theatre Where Lincoln Was Shot
16th president of the United States (1809–1865)
| Abraham Lincoln | |
|---|---|
 Portrait by Alexander Gardner, November 1863 | |
| 16th President of the United States | |
| In office March 4, 1861 – April 15, 1865 | |
| Vice President |
|
| Preceded by | James Buchanan |
| Succeeded by | Andrew Johnson |
| Member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Illinois's 7th district | |
| In office March 4, 1847 – March 3, 1849 | |
| Preceded by | John Henry |
| Succeeded by | Thomas L. Harris |
| Member of the Illinois House of Representatives from Sangamon County | |
| In office December 1, 1834 – December 4, 1842 | |
| Personal details | |
| Born | (1809-02-12)February 12, 1809 Hodgenville, Kentucky, U.S. |
| Died | April 15, 1865(1865-04-15) (aged 56) Washington, D.C., U.S. |
| Cause of death | Assassinated (gunshot wound to the head) |
| Resting place | Lincoln Tomb |
| Political party |
|
| Other political affiliations | National Union (Republican) (1864–1865) |
| Height | 6 ft 4 in (193 cm)[1] |
| Spouse(s) | Mary Todd (m. ) |
| Children |
|
| Parent(s) | Thomas Lincoln Nancy Hanks |
| Relatives | Lincoln family |
| Occupation |
|
| Signature | |
| Military service | |
| Branch/service | Illinois Militia |
| Years of service | 1832 |
| Rank |
|
| Battles/wars |
|
Abraham Lincoln (; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation through the American Civil War and succeeded in preserving the Union, abolishing slavery, bolstering the federal government, and modernizing the U.S. economy.
Lincoln was born into poverty in a log cabin and was raised on the frontier primarily in Indiana. He was self-educated and became a lawyer, Whig Party leader, Illinois state legislator, and U.S. Congressman from Illinois. In 1849, he returned to his law practice but became vexed by the opening of additional lands to slavery as a result of the Kansas–Nebraska Act. He reentered politics in 1854, becoming a leader in the new Republican Party, and he reached a national audience in the 1858 debates against Stephen Douglas. Lincoln ran for President in 1860, sweeping the North in victory. Pro-slavery elements in the South equated his success with the North's rejection of their right to practice slavery, and southern states began seceding from the Union. To secure its independence, the new Confederate States fired on Fort Sumter, a U.S. fort in the South, and Lincoln called up forces to suppress the rebellion and restore the Union.
Lincoln, a moderate Republican, had to navigate a contentious array of factions with friends and opponents from both the Democratic and Republican parties. His allies, the War Democrats and the Radical Republicans, demanded harsh treatment of the Southern Confederates. Anti-war Democrats (called "Copperheads") despised Lincoln, and irreconcilable pro-Confederate elements plotted his assassination. He managed the factions by exploiting their mutual enmity, carefully distributing political patronage, and by appealing to the American people. His Gettysburg Address appealed to nationalistic, republican, egalitarian, libertarian, and democratic sentiments. Lincoln scrutinized the strategy and tactics in the war effort, including the selection of generals and the naval blockade of the South's trade. He suspended habeas corpus in Maryland, and he averted British intervention by defusing the Trent Affair. He engineered the end to slavery with his Emancipation Proclamation, including his order that the Army and Navy liberate, protect, and recruit former slaves. He also encouraged border states to outlaw slavery, and promoted the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which outlawed slavery across the country.
Lincoln managed his own successful re-election campaign. He sought to heal the war-torn nation through reconciliation. On April 14, 1865, just days after the war's end at Appomattox, he was attending a play at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C., with his wife Mary when he was fatally shot by Confederate sympathizer John Wilkes Booth. Lincoln is remembered as a martyr and hero of the United States and is often ranked as the greatest president in American history.
Family and childhood
Early life
Abraham Lincoln was born on February 12, 1809, the second child of Thomas Lincoln and Nancy Hanks Lincoln, in a log cabin on Sinking Spring Farm near Hodgenville, Kentucky.[2] He was a descendant of Samuel Lincoln, an Englishman who migrated from Hingham, Norfolk, to its namesake, Hingham, Massachusetts, in 1638. The family then migrated west, passing through New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Virginia.[3] Lincoln's paternal grandparents, his namesake Captain Abraham Lincoln and wife Bathsheba (née Herring) moved the family from Virginia to Jefferson County, Kentucky.[b] The captain was killed in an Indian raid in 1786.[5] His children, including eight-year-old Thomas, Abraham's father, witnessed the attack.[6] [c] Thomas then worked at odd jobs in Kentucky and Tennessee before the family settled in Hardin County, Kentucky, in the early 1800s.[6]
The heritage of Lincoln's mother Nancy remains unclear, but it is widely assumed that she was the daughter of Lucy Hanks.[8] Thomas and Nancy married on June 12, 1806, in Washington County, and moved to Elizabethtown, Kentucky.[9] They had three children: Sarah, Abraham, and Thomas, who died as infant.[10]
Thomas Lincoln bought or leased farms in Kentucky before losing all but 200 acres (81 ha) of his land in court disputes over property titles.[11] In 1816, the family moved to Indiana where the land surveys and titles were more reliable.[12] Indiana was a "free" (non-slaveholding) territory, and they settled in an "unbroken forest"[13] in Hurricane Township, Perry County, Indiana.[14] [d] In 1860, Lincoln noted that the family's move to Indiana was "partly on account of slavery", but mainly due to land title difficulties.[16]

In Kentucky and Indiana, Thomas worked as a farmer, cabinetmaker, and carpenter.[17] At various times, he owned farms, livestock, and town lots, paid taxes, sat on juries, appraised estates, and served on county patrols. Thomas and Nancy were members of a Separate Baptists church, which forbade alcohol, dancing, and slavery.[18]
Overcoming financial challenges, Thomas in 1827 obtained clear title to 80 acres (32 ha) in Indiana, an area which became the Little Pigeon Creek Community.[19]
Mother's death
On October 5, 1818, Nancy Lincoln succumbed to milk sickness, leaving 11-year-old Sarah in charge of a household including her father, 9-year-old Abraham, and Nancy's 19-year-old orphan cousin, Dennis Hanks.[20] Ten years later, on January 20, 1828, Sarah died while giving birth to a stillborn son, devastating Lincoln.[21]
On December 2, 1819, Thomas married Sarah Bush Johnston, a widow from Elizabethtown, Kentucky, with three children of her own.[22] Abraham became close to his stepmother and called her "Mother".[23] Lincoln disliked the hard labor associated with farm life. His family even said he was lazy, for all his "reading, scribbling, writing, ciphering, writing Poetry, etc".[24] His stepmother acknowledged he did not enjoy "physical labor", but loved to read.[25]
Education and move to Illinois
Lincoln was largely self-educated.[26] His formal schooling was from itinerant teachers. It included two short stints in Kentucky, where he learned to read but probably not to write, at age seven,[27] and in Indiana, where he went to school sporadically due to farm chores, for a total of less than 12 months in aggregate by the age of 15.[28] He persisted as an avid reader and retained a lifelong interest in learning.[29] Family, neighbors, and schoolmates recalled that his reading included the King James Bible, Aesop's Fables, John Bunyan's The Pilgrim's Progress, Daniel Defoe's Robinson Crusoe, and The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin.[30]
As a teen, Lincoln took responsibility for chores and customarily gave his father all earnings from work outside the home until he was 21.[31] Lincoln was tall, strong, and athletic, and became adept at using an ax.[32] He was an active wrestler during his youth and trained in the rough catch-as-catch-can style (also known as catch wrestling). He became county wrestling champion at the age of 21.[33] He gained a reputation for strength and audacity after winning a wrestling match with the renowned leader of ruffians known as "the Clary's Grove Boys".[34]
In March 1830, fearing another milk sickness outbreak, several members of the extended Lincoln family, including Abraham, moved west to Illinois, a free state, and settled in Macon County.[35] [e] Abraham then became increasingly distant from Thomas, in part due to his father's lack of education.[37] In 1831, as Thomas and other family prepared to move to a new homestead in Coles County, Illinois, Abraham struck out on his own.[38] He made his home in New Salem, Illinois, for six years.[39] Lincoln and some friends took goods by flatboat to New Orleans, Louisiana, where he was first exposed to slavery.[40]
In 1865, Lincoln was asked how he came to acquire his rhetorical skills. He answered that in the practice of law he frequently came across the word "demonstrate" but had insufficient understanding of the term. So, he left Springfield for his father's home to study until he "could give any proposition in the six books of Euclid [here, referencing Euclid's Elements] at sight."[41]
Marriage and children

1864 photo of President Lincoln with youngest son, Tad

Lincoln's first romantic interest was Ann Rutledge, whom he met when he moved to New Salem. By 1835, they were in a relationship but not formally engaged.[42] She died on August 25, 1835, most likely of typhoid fever.[43] In the early 1830s, he met Mary Owens from Kentucky.[44]
Late in 1836, Lincoln agreed to a match with Owens if she returned to New Salem. Owens arrived that November and he courted her for a time; however, they both had second thoughts. On August 16, 1837, he wrote Owens a letter saying he would not blame her if she ended the relationship, and she never replied.[45]
In 1839, Lincoln met Mary Todd in Springfield, Illinois, and the following year they became engaged.[46] She was the daughter of Robert Smith Todd, a wealthy lawyer and businessman in Lexington, Kentucky.[47] A wedding set for January 1, 1841, was canceled at Lincoln's request, but they reconciled and married on November 4, 1842, in the Springfield mansion of Mary's sister.[48] While anxiously preparing for the nuptials, he was asked where he was going and replied, "To hell, I suppose."[49] In 1844, the couple bought a house in Springfield near his law office. Mary kept house with the help of a hired servant and a relative.[50]
Lincoln was an affectionate husband and father of four sons, though his work regularly kept him away from home. The oldest, Robert Todd Lincoln, was born in 1843 and was the only child to live to maturity. Edward Baker Lincoln (Eddie), born in 1846, died February 1, 1850, probably of tuberculosis. Lincoln's third son, "Willie" Lincoln was born on December 21, 1850, and died of a fever at the White House on February 20, 1862. The youngest, Thomas "Tad" Lincoln, was born on April 4, 1853, and survived his father but died of heart failure at age 18 on July 16, 1871.[51] [f] Lincoln "was remarkably fond of children"[53] and the Lincolns were not considered to be strict with their own.[54] In fact, Lincoln's law partner William H. Herndon would grow irritated when Lincoln would bring his children to the law office. Their father, it seemed, was often too absorbed in his work to notice his children's behavior. Herndon recounted, "I have felt many and many a time that I wanted to wring their little necks, and yet out of respect for Lincoln I kept my mouth shut. Lincoln did not note what his children were doing or had done."[55]
The deaths of their sons, Eddie and Willie, had profound effects on both parents. Lincoln suffered from "melancholy", a condition now thought to be clinical depression.[56] Later in life, Mary struggled with the stresses of losing her husband and sons, and Robert committed her for a time to an asylum in 1875.[57]
Early career and militia service
In 1832, Lincoln joined with a partner, Denton Offutt, in the purchase of a general store on credit in New Salem.[58] Although the economy was booming, the business struggled and Lincoln eventually sold his share. That March he entered politics, running for the Illinois General Assembly, advocating navigational improvements on the Sangamon River. He could draw crowds as a raconteur, but he lacked the requisite formal education, powerful friends, and money, and lost the election.[59]
Lincoln briefly interrupted his campaign to serve as a captain in the Illinois Militia during the Black Hawk War.[60] In his first campaign speech after returning, he observed a supporter in the crowd under attack, grabbed the assailant by his "neck and the seat of his trousers", and tossed him.[35] Lincoln finished eighth out of 13 candidates (the top four were elected), though he received 277 of the 300 votes cast in the New Salem precinct.[61]
Lincoln served as New Salem's postmaster and later as county surveyor, but continued his voracious reading, and decided to become a lawyer.[62] Rather than studying in the office of an established attorney, as was the custom, Lincoln borrowed legal texts from attorneys John Todd Stuart and Thomas Drummond, purchased books including Blackstone's Commentaries and Chitty's Pleadings, and read law on his own.[62] He later said of his legal education that "I studied with nobody."[63]
Illinois state legislature (1834–1842)

Lincoln's second state house campaign in 1834, this time as a Whig, was a success over a powerful Whig opponent.[64] Then followed his four terms in the Illinois House of Representatives for Sangamon County.[65] He championed construction of the Illinois and Michigan Canal, and later was a Canal Commissioner.[66] He voted to expand suffrage beyond white landowners to all white males, but adopted a "free soil" stance opposing both slavery and abolition.[67] In 1837 he declared, "[The] Institution of slavery is founded on both injustice and bad policy, but the promulgation of abolition doctrines tends rather to increase than abate its evils."[68] He echoed Henry Clay's support for the American Colonization Society which advocated a program of abolition in conjunction with settling freed slaves in Liberia.[69]
He was admitted to the Illinois bar in 1836,[70] and moved to Springfield and began to practice law under John T. Stuart, Mary Todd's cousin.[71] Lincoln emerged as a formidable trial combatant during cross-examinations and closing arguments. He partnered several years with Stephen T. Logan, and in 1844 began his practice with William Herndon, "a studious young man".[72]
U.S. House of Representatives (1847–1849)

True to his record, Lincoln professed to friends in 1861 to be "an old line Whig, a disciple of Henry Clay".[73] Their party favored economic modernization in banking, tariffs to fund internal improvements including railroads, and urbanization.[74]
In 1843, Lincoln sought the Whig nomination for Illinois' 7th district seat in the U.S. House of Representatives; he was defeated by John J. Hardin though he prevailed with the party in limiting Hardin to one term. Lincoln not only pulled off his strategy of gaining the nomination in 1846 but also won the election. He was the only Whig in the Illinois delegation, but as dutiful as any participated in almost all votes and made speeches that toed the party line.[75] He was assigned to the Committee on Post Office and Post Roads and the Committee on Expenditures in the War Department.[76] Lincoln teamed with Joshua R. Giddings on a bill to abolish slavery in the District of Columbia with compensation for the owners, enforcement to capture fugitive slaves, and a popular vote on the matter. He dropped the bill when it eluded Whig support.[77]
Political views
On foreign and military policy, Lincoln spoke against the Mexican–American War, which he imputed to President James K. Polk's desire for "military glory—that attractive rainbow, that rises in showers of blood".[78] He supported the Wilmot Proviso, a failed proposal to ban slavery in any U.S. territory won from Mexico.[79]
Lincoln emphasized his opposition to Polk by drafting and introducing his Spot Resolutions. The war had begun with a Mexican slaughter of American soldiers in territory disputed by Mexico, and Polk insisted that Mexican soldiers had "invaded our territory and shed the blood of our fellow-citizens on our own soil".[80] Lincoln demanded that Polk show Congress the exact spot on which blood had been shed and prove that the spot was on American soil.[81] The resolution was ignored in both Congress and the national papers, and it cost Lincoln political support in his district. One Illinois newspaper derisively nicknamed him "spotty Lincoln".[82] Lincoln later regretted some of his statements, especially his attack on presidential war-making powers.[83]
Lincoln had pledged in 1846 to serve only one term in the House. Realizing Clay was unlikely to win the presidency, he supported General Zachary Taylor for the Whig nomination in the 1848 presidential election.[84] Taylor won and Lincoln hoped in vain to be appointed Commissioner of the General Land Office.[85] The administration offered to appoint him secretary or governor of the Oregon Territory as consolation.[86] This distant territory was a Democratic stronghold, and acceptance of the post would have disrupted his legal and political career in Illinois, so he declined and resumed his law practice.[87]
Prairie lawyer

In his Springfield practice, Lincoln handled "every kind of business that could come before a prairie lawyer".[88] Twice a year he appeared for 10 consecutive weeks in county seats in the Midstate county courts; this continued for 16 years.[89] Lincoln handled transportation cases in the midst of the nation's western expansion, particularly river barge conflicts under the many new railroad bridges. As a riverboat man, Lincoln initially favored those interests, but ultimately represented whoever hired him.[90] He later represented a bridge company against a riverboat company in Hurd v. Rock Island Bridge Company, a landmark case involving a canal boat that sank after hitting a bridge.[91] In 1849, he received a patent for a flotation device for the movement of boats in shallow water. The idea was never commercialized, but it made Lincoln the only president to hold a patent.[92]
Lincoln appeared before the Illinois Supreme Court in 175 cases; he was sole counsel in 51 cases, of which 31 were decided in his favor.[93] From 1853 to 1860, one of his largest clients was the Illinois Central Railroad.[94] His legal reputation gave rise to the nickname "Honest Abe".[95]
Lincoln argued in an 1858 criminal trial, defending William "Duff" Armstrong, who was on trial for the murder of James Preston Metzker.[96] The case is famous for Lincoln's use of a fact established by judicial notice to challenge the credibility of an eyewitness. After an opposing witness testified to seeing the crime in the moonlight, Lincoln produced a Farmers' Almanac showing the moon was at a low angle, drastically reducing visibility. Armstrong was acquitted.[96]
Leading up to his presidential campaign, Lincoln elevated his profile in an 1859 murder case, with his defense of Simeon Quinn "Peachy" Harrison who was a third cousin;[g] Harrison was also the grandson of Lincoln's political opponent, Rev. Peter Cartwright.[98] Harrison was charged with the murder of Greek Crafton who, as he lay dying of his wounds, confessed to Cartwright that he had provoked Harrison.[99] Lincoln angrily protested the judge's initial decision to exclude Cartwright's testimony about the confession as inadmissible hearsay. Lincoln argued that the testimony involved a dying declaration and was not subject to the hearsay rule. Instead of holding Lincoln in contempt of court as expected, the judge, a Democrat, reversed his ruling and admitted the testimony into evidence, resulting in Harrison's acquittal.[96]
Republican politics (1854–1860)
Emergence as Republican leader

The debate over the status of slavery in the territories failed to alleviate tensions between the slave-holding South and the free North, with the failure of the Compromise of 1850, a legislative package designed to address the issue.[100] In his 1852 eulogy for Clay, Lincoln highlighted the latter's support for gradual emancipation and opposition to "both extremes" on the slavery issue.[101] As the slavery debate in the Nebraska and Kansas territories became particularly acrimonious, Illinois Senator Stephen A. Douglas proposed popular sovereignty as a compromise; the measure would allow the electorate of each territory to decide the status of slavery. The legislation alarmed many Northerners, who sought to prevent the resulting spread of slavery, but Douglas's Kansas–Nebraska Act narrowly passed Congress in May 1854.[102]
Lincoln did not comment on the act until months later in his "Peoria Speech" in October 1854. Lincoln then declared his opposition to slavery which he repeated en route to the presidency.[103] He said the Kansas Act had a "declared indifference, but as I must think, a covert real zeal for the spread of slavery. I cannot but hate it. I hate it because of the monstrous injustice of slavery itself. I hate it because it deprives our republican example of its just influence in the world ..."[104] Lincoln's attacks on the Kansas–Nebraska Act marked his return to political life.[105]
Nationally, the Whigs were irreparably split by the Kansas–Nebraska Act and other efforts to compromise on the slavery issue. Reflecting on the demise of his party, Lincoln wrote in 1855, "I think I am a Whig, but others say there are no Whigs, and that I am an abolitionist...I do no more than oppose the extension of slavery."[106] The new Republican Party was formed as a northern party dedicated to antislavery, drawing from the antislavery wing of the Whig Party, and combining Free Soil, Liberty, and antislavery Democratic Party members,[107] Lincoln resisted early Republican entreaties, fearing that the new party would become a platform for extreme abolitionists.[108] Lincoln held out hope for rejuvenating the Whigs, though he lamented his party's growing closeness with the nativist Know Nothing movement.[109]
In 1854 Lincoln was elected to the Illinois legislature but declined to take his seat. The year's elections showed the strong opposition to the Kansas–Nebraska Act, and in the aftermath, Lincoln sought election to the United States Senate.[105] At that time, senators were elected by the state legislature.[110] After leading in the first six rounds of voting, he was unable to obtain a majority. Lincoln instructed his backers to vote for Lyman Trumbull. Trumbull was an antislavery Democrat, and had received few votes in the earlier ballots; his supporters, also antislavery Democrats, had vowed not to support any Whig. Lincoln's decision to withdraw enabled his Whig supporters and Trumbull's antislavery Democrats to combine and defeat the mainstream Democratic candidate, Joel Aldrich Matteson.[111]
1856 campaign
Violent political confrontations in Kansas continued, and opposition to the Kansas–Nebraska Act remained strong throughout the North. As the 1856 elections approached, Lincoln joined the Republicans and attended the Bloomington Convention, which formally established the Illinois Republican Party. The convention platform endorsed Congress's right to regulate slavery in the territories and backed the admission of Kansas as a free state. Lincoln gave the final speech of the convention supporting the party platform and called for the preservation of the Union.[112] At the June 1856 Republican National Convention, though Lincoln received support to run as vice president, John C. Frémont and William Dayton comprised the ticket, which Lincoln supported throughout Illinois. The Democrats nominated former Secretary of State James Buchanan and the Know-Nothings nominated former Whig President Millard Fillmore.[113] Buchanan prevailed, while Republican William Henry Bissell won election as Governor of Illinois, and Lincoln became a leading Republican in Illinois.[114] [h]

Dred Scott v. Sandford
Dred Scott was a slave whose master took him from a slave state to a free territory under the Missouri Compromise. After Scott was returned to the slave state he petitioned a federal court for his freedom. His petition was denied in Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857).[i] Supreme Court Chief Justice Roger B. Taney in the decision wrote that blacks were not citizens and derived no rights from the Constitution. While many Democrats hoped that Dred Scott would end the dispute over slavery in the territories, the decision sparked further outrage in the North.[117] Lincoln denounced it as the product of a conspiracy of Democrats to support the Slave Power.[118] He argued the decision was at variance with the Declaration of Independence; he said that while the founding fathers did not believe all men equal in every respect, they believed all men were equal "in certain inalienable rights, among which are life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness".[119]
Lincoln–Douglas debates and Cooper Union speech
In 1858 Douglas was up for re-election in the U.S. Senate, and Lincoln hoped to defeat him. Many in the party felt that a former Whig should be nominated in 1858, and Lincoln's 1856 campaigning and support of Trumbull had earned him a favor.[120] Some eastern Republicans supported Douglas from his opposition to the Lecompton Constitution and admission of Kansas as a slave state.[121] Many Illinois Republicans resented this eastern interference. For the first time, Illinois Republicans held a convention to agree upon a Senate candidate, and Lincoln won the nomination with little opposition.[122]

Abraham Lincoln (1860) by Mathew Brady, taken the day of the Cooper Union speech
Lincoln accepted the nomination with great enthusiasm and zeal. After his nomination he delivered his House Divided Speech, with the biblical reference Mark 3:25, "A house divided against itself cannot stand. I believe this government cannot endure permanently half slave and half free. I do not expect the Union to be dissolved—I do not expect the house to fall—but I do expect it will cease to be divided. It will become all one thing, or all the other."[123] The speech created a stark image of the danger of disunion.[124] The stage was then set for the election of the Illinois legislature which would, in turn, select Lincoln or Douglas.[125] When informed of Lincoln's nomination, Douglas stated, "[Lincoln] is the strong man of the party ... and if I beat him, my victory will be hardly won."[126]
The Senate campaign featured seven debates between Lincoln and Douglas. These were the most famous political debates in American history; they had an atmosphere akin to a prizefight and drew crowds in the thousands.[127] The principals stood in stark contrast both physically and politically. Lincoln warned that Douglas' "Slave Power" was threatening the values of republicanism, and accused Douglas of distorting the Founding Fathers' premise that all men are created equal. Douglas emphasized his Freeport Doctrine, that local settlers were free to choose whether to allow slavery and accused Lincoln of having joined the abolitionists.[128] Lincoln's argument assumed a moral tone, as he claimed Douglas represented a conspiracy to promote slavery. Douglas's argument was more legal, claiming that Lincoln was defying the authority of the U.S. Supreme Court in the Dred Scott decision.[129]
Though the Republican legislative candidates won more popular votes, the Democrats won more seats, and the legislature re-elected Douglas. Lincoln's articulation of the issues gave him a national political presence.[130] In May 1859, Lincoln purchased the Illinois Staats-Anzeiger, a German-language newspaper that was consistently supportive; most of the state's 130,000 German Americans voted Democratically but the German-language paper mobilized Republican support.[131] In the aftermath of the 1858 election, newspapers frequently mentioned Lincoln as a potential Republican presidential candidate, rivaled by William H. Seward, Salmon P. Chase, Edward Bates, and Simon Cameron. While Lincoln was popular in the Midwest, he lacked support in the Northeast and was unsure whether to seek office.[132] In January 1860, Lincoln told a group of political allies that he would accept the nomination if offered, and in the following months' several local papers endorsed his candidacy.[133]
Traveling untiringly Lincoln made about fifty speeches. By their quality and simplicity, he quickly became the champion of the Republican party. However, unlike his overwhelming support in the Midwestern United States his support in the east was not as great, where he sometimes encountered a lack of appreciation and in some quarters was met with much indifference. Horace Greeley, editor of the New York Tribune, at that time wrote up an unflattering account of Lincoln's compromising position on slavery and his reluctance to challenge the court's Dred-Scott ruling, which was promptly used against him by his political rivals.[134] [135]
On February 27, 1860, powerful New York Republicans invited Lincoln to give a speech at Cooper Union, in which he argued that the Founding Fathers of the United States had little use for popular sovereignty and had repeatedly sought to restrict slavery. He insisted that morality required opposition to slavery, and rejected any "groping for some middle ground between the right and the wrong".[136] Many in the audience thought he appeared awkward and even ugly.[137] But Lincoln demonstrated intellectual leadership that brought him into contention. Journalist Noah Brooks reported, "No man ever before made such an impression on his first appeal to a New York audience."[138]
Historian David Herbert Donald described the speech as a "superb political move for an unannounced candidate, to appear in one rival's (Seward) own state at an event sponsored by the second rival's (Chase) loyalists, while not mentioning either by name during its delivery".[139] In response to an inquiry about his ambitions, Lincoln said, "The taste is in my mouth a little."[140]
1860 presidential election

A Timothy Cole wood engraving taken from a May 20, 1860, ambrotype of Lincoln, two days following his nomination for president
On May 9–10, 1860, the Illinois Republican State Convention was held in Decatur.[141] Lincoln's followers organized a campaign team led by David Davis, Norman Judd, Leonard Swett, and Jesse DuBois, and Lincoln received his first endorsement.[142] Exploiting his embellished frontier legend (clearing land and splitting fence rails), Lincoln's supporters adopted the label of "The Rail Candidate".[143] In 1860, Lincoln described himself: "I am in height, six feet, four inches, nearly; lean in flesh, weighing, on an average, one hundred and eighty pounds; dark complexion, with coarse black hair, and gray eyes."[144] Michael Martinez wrote about the effective imaging of Lincoln by his campaign. At times he was presented as the plain-talking "Rail Splitter" and at other times he was "Honest Abe", unpolished but trustworthy.[145]
On May 18, at the Republican National Convention in Chicago, Lincoln won the nomination on the third ballot, beating candidates such as Seward and Chase. A former Democrat, Hannibal Hamlin of Maine, was nominated for vice president to balance the ticket. Lincoln's success depended on his campaign team, his reputation as a moderate on the slavery issue, and his strong support for internal improvements and the tariff.[146] Pennsylvania put him over the top, led by the state's iron interests who were reassured by his tariff support.[147] Lincoln's managers had focused on this delegation while honoring Lincoln's dictate to "Make no contracts that will bind me".[148]
As the Slave Power tightened its grip on the national government, most Republicans agreed with Lincoln that the North was the aggrieved party. Throughout the 1850s, Lincoln had doubted the prospects of civil war, and his supporters rejected claims that his election would incite secession.[149] When Douglas was selected as the candidate of the Northern Democrats, delegates from eleven slave states walked out of the Democratic convention; they opposed Douglas's position on popular sovereignty, and selected incumbent Vice President John C. Breckinridge as their candidate.[150] A group of former Whigs and Know Nothings formed the Constitutional Union Party and nominated John Bell of Tennessee. Lincoln and Douglas competed for votes in the North, while Bell and Breckinridge primarily found support in the South.[120]

The Rail Candidate—Lincoln's 1860 platform, portrayed as being held up by a slave and his party
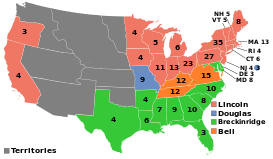
In 1860, northern and western electoral votes (shown in red) put Lincoln into the White House.
Prior to the Republican convention, the Lincoln campaign began cultivating a nationwide youth organization, the Wide Awakes, which it used to generate popular support throughout the country to spearhead voter registration drives, thinking that new voters and young voters tended to embrace new parties.[151] People of the Northern states knew the Southern states would vote against Lincoln and rallied supporters for Lincoln.[152]
As Douglas and the other candidates campaigned, Lincoln gave no speeches, relying on the enthusiasm of the Republican Party. The party did the leg work that produced majorities across the North and produced an abundance of campaign posters, leaflets, and newspaper editorials. Republican speakers focused first on the party platform, and second on Lincoln's life story, emphasizing his childhood poverty. The goal was to demonstrate the power of "free labor", which allowed a common farm boy to work his way to the top by his own efforts.[153] The Republican Party's production of campaign literature dwarfed the combined opposition; a Chicago Tribune writer produced a pamphlet that detailed Lincoln's life and sold 100,000–200,000 copies.[154] Though he did not give public appearances, many sought to visit him and write him. In the runup to the election, he took an office in the Illinois state capitol to deal with the influx of attention. He also hired John George Nicolay as his personal secretary, who would remain in that role during the presidency.[155]
On November 6, 1860, Lincoln was elected the 16th president. He was the first Republican president and his victory was entirely due to his support in the North and West. No ballots were cast for him in 10 of the 15 Southern slave states, and he won only two of 996 counties in all the Southern states, an omen of the impending Civil War.[156] [157] Lincoln received 1,866,452 votes, or 39.8% of the total in a four-way race, carrying the free Northern states, as well as California and Oregon.[158] His victory in the electoral college was decisive: Lincoln had 180 votes to 123 for his opponents.[159]
Presidency (1861–1865)
Secession and inauguration

Headlines on the day of Lincoln's inauguration portended hostilities with the Confederacy, Fort Sumter being attacked less than six weeks later.[160]
The South was outraged by Lincoln's election, and in response secessionists implemented plans to leave the Union before he took office in March 1861.[161] On December 20, 1860, South Carolina took the lead by adopting an ordinance of secession; by February 1, 1861, Florida, Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas followed.[162] Six of these states declared themselves to be a sovereign nation, the Confederate States of America, and adopted a constitution.[163] The upper South and border states (Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, Kentucky, Missouri, and Arkansas) initially rejected the secessionist appeal.[164] President Buchanan and President-elect Lincoln refused to recognize the Confederacy, declaring secession illegal.[165] The Confederacy selected Jefferson Davis as its provisional president on February 9, 1861.[166]
Attempts at compromise followed but Lincoln and the Republicans rejected the proposed Crittenden Compromise as contrary to the Party's platform of free-soil in the territories.[167] Lincoln said, "I will suffer death before I consent ... to any concession or compromise which looks like buying the privilege to take possession of this government to which we have a constitutional right."[168]
Lincoln tacitly supported the Corwin Amendment to the Constitution, which passed Congress and was awaiting ratification by the states when Lincoln took office. That doomed amendment would have protected slavery in states where it already existed.[169] A few weeks before the war, Lincoln sent a letter to every governor informing them Congress had passed a joint resolution to amend the Constitution.[170]

En route to his inauguration, Lincoln addressed crowds and legislatures across the North.[171] He gave a particularly emotional farewell address upon leaving Springfield; he would never again return to Springfield alive.[172] [173] The president-elect evaded suspected assassins in Baltimore. On February 23, 1861, he arrived in disguise in Washington, D.C., which was placed under substantial military guard.[174] Lincoln directed his inaugural address to the South, proclaiming once again that he had no inclination to abolish slavery in the Southern states:
Apprehension seems to exist among the people of the Southern States that by the accession of a Republican Administration their property and their peace and personal security are to be endangered. There has never been any reasonable cause for such apprehension. Indeed, the most ample evidence to the contrary has all the while existed and been open to their inspection. It is found in nearly all the published speeches of him who now addresses you. I do but quote from one of those speeches when I declare that "I have no purpose, directly or indirectly, to interfere with the institution of slavery in the States where it exists. I believe I have no lawful right to do so, and I have no inclination to do so."
Lincoln cited his plans for banning the expansion of slavery as the key source of conflict between North and South, stating "One section of our country believes slavery is right and ought to be extended, while the other believes it is wrong and ought not to be extended. This is the only substantial dispute." The president ended his address with an appeal to the people of the South: "We are not enemies, but friends. We must not be enemies ... The mystic chords of memory, stretching from every battlefield, and patriot grave, to every living heart and hearthstone, all over this broad land, will yet swell the chorus of the Union, when again touched, as surely they will be, by the better angels of our nature."[176] The failure of the Peace Conference of 1861 signaled that legislative compromise was impossible. By March 1861, no leaders of the insurrection had proposed rejoining the Union on any terms. Meanwhile, Lincoln and the Republican leadership agreed that the dismantling of the Union could not be tolerated.[177] In his second inaugural address, Lincoln looked back on the situation at the time and said: "Both parties deprecated war, but one of them would make war rather than let the Nation survive, and the other would accept war rather than let it perish, and the war came."
Civil War

Major Robert Anderson, commander of the Union's Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina, sent a request for provisions to Washington, and Lincoln's order to meet that request was seen by the secessionists as an act of war. On April 12, 1861, Confederate forces fired on Union troops at Fort Sumter and began the fight. Historian Allan Nevins argued that the newly inaugurated Lincoln made three miscalculations: underestimating the gravity of the crisis, exaggerating the strength of Unionist sentiment in the South, and overlooking Southern Unionist opposition to an invasion.[178]
William Tecumseh Sherman talked to Lincoln during inauguration week and was "sadly disappointed" at his failure to realize that "the country was sleeping on a volcano" and that the South was preparing for war.[179] Donald concludes that, "His repeated efforts to avoid collision in the months between inauguration and the firing on Ft. Sumter showed he adhered to his vow not to be the first to shed fraternal blood. But he also vowed not to surrender the forts. The only resolution of these contradictory positions was for the confederates to fire the first shot; they did just that."[180]
On April 15, Lincoln called on the states to send a total of 75,000 volunteer troops to recapture forts, protect Washington, and "preserve the Union", which, in his view, remained intact despite the seceding states. This call forced states to choose sides. Virginia seceded and was rewarded with the designation of Richmond as the Confederate capital, despite its exposure to Union lines. North Carolina, Tennessee, and Arkansas followed over the following two months. Secession sentiment was strong in Missouri and Maryland, but did not prevail; Kentucky remained neutral.[181] The Fort Sumter attack rallied Americans north of the Mason-Dixon line to defend the nation.
As States sent Union regiments south, on April 19, Baltimore mobs in control of the rail links attacked Union troops who were changing trains. Local leaders' groups later burned critical rail bridges to the capital and the Army responded by arresting local Maryland officials. Lincoln suspended the writ of habeas corpus where needed for the security of troops trying to reach Washington.[182] John Merryman, one Maryland official hindering the U.S. troop movements, petitioned Supreme Court Chief Justice Roger B. Taney to issue a writ of habeas corpus. In June Taney, ruling only for the lower circuit court in ex parte Merryman, issued the writ which he felt could only be suspended by Congress. Lincoln persisted with the policy of suspension in select areas.[183] [184]
Union military strategy
Lincoln took executive control of the war and shaped the Union military strategy. He responded to the unprecedented political and military crisis as commander-in-chief by exercising unprecedented authority. He expanded his war powers, imposed a blockade on Confederate ports, disbursed funds before appropriation by Congress, suspended habeas corpus, and arrested and imprisoned thousands of suspected Confederate sympathizers. Lincoln gained the support of Congress and the northern public for these actions. Lincoln also had to reinforce Union sympathies in the border slave states and keep the war from becoming an international conflict.[185]

It was clear from the outset that bipartisan support was essential to success, and that any compromise alienated factions on both sides of the aisle, such as the appointment of Republicans and Democrats to command positions. Copperheads criticized Lincoln for refusing to compromise on slavery. The Radical Republicans criticized him for moving too slowly in abolishing slavery.[186] On August 6, 1861, Lincoln signed the Confiscation Act that authorized judicial proceedings to confiscate and free slaves who were used to support the Confederates. The law had little practical effect, but it signaled political support for abolishing slavery.[187]
In August 1861, General John C. Frémont, the 1856 Republican presidential nominee, without consulting Washington, issued a martial edict freeing slaves of the rebels. Lincoln canceled the illegal proclamation as politically motivated and lacking military necessity.[188] As a result, Union enlistments from Maryland, Kentucky, and Missouri increased by over 40,000.[189]
Internationally, Lincoln wanted to forestall foreign military aid to the Confederacy.[190] He relied on his combative Secretary of State William Seward while working closely with Senate Foreign Relations Committee chairman Charles Sumner.[191] In the 1861 Trent Affair which threatened war with Great Britain, the U.S. Navy illegally intercepted a British mail ship, the Trent, on the high seas and seized two Confederate envoys; Britain protested vehemently while the U.S. cheered. Lincoln ended the crisis by releasing the two diplomats. Biographer James G. Randall dissected Lincoln's successful techniques:[192]
his restraint, his avoidance of any outward expression of truculence, his early softening of State Department's attitude toward Britain, his deference toward Seward and Sumner, his withholding of his paper prepared for the occasion, his readiness to arbitrate, his golden silence in addressing Congress, his shrewdness in recognizing that war must be averted, and his clear perception that a point could be clinched for America's true position at the same time that satisfaction was given to a friendly country.
Lincoln painstakingly monitored the telegraph reports coming into the War Department. He tracked all phases of the effort, consulting with governors, and selecting generals based on their success, their state, and their party. In January 1862, after complaints of inefficiency and profiteering in the War Department, Lincoln replaced War Secretary Simon Cameron with Edwin Stanton. Stanton centralized the War Department's activities, auditing and canceling contracts, saving the federal government $17,000,000.[193] Stanton was a staunch Unionist, pro-business, conservative Democrat who gravitated toward the Radical Republican faction. He worked more often and more closely with Lincoln than any other senior official. "Stanton and Lincoln virtually conducted the war together", say Thomas and Hyman.[194]
Lincoln's war strategy embraced two priorities: ensuring that Washington was well-defended and conducting an aggressive war effort for a prompt, decisive victory.[j] Twice a week, Lincoln met with his cabinet in the afternoon. Occasionally Mary prevailed on him to take a carriage ride, concerned that he was working too hard.[196] For his edification Lincoln relied upon a book by his chief of staff General Henry Halleck entitled Elements of Military Art and Science; Halleck was a disciple of the European strategist Antoine-Henri Jomini. Lincoln began to appreciate the critical need to control strategic points, such as the Mississippi River.[197] Lincoln saw the importance of Vicksburg and understood the necessity of defeating the enemy's army, rather than simply capturing territory.[198]
General McClellan
After the Union rout at Bull Run and Winfield Scott's retirement, Lincoln appointed Major General George B. McClellan general-in-chief.[199] McClellan then took months to plan his Virginia Peninsula Campaign. McClellan's slow progress frustrated Lincoln, as did his position that no troops were needed to defend Washington. McClellan, in turn, blamed the failure of the campaign on Lincoln's reservation of troops for the capitol.[200]

In 1862 Lincoln removed McClellan for the general's continued inaction. He elevated Henry Halleck in July and appointed John Pope as head of the new Army of Virginia.[201] Pope satisfied Lincoln's desire to advance on Richmond from the north, thus protecting Washington from counterattack.[202] But Pope was then soundly defeated at the Second Battle of Bull Run in the summer of 1862, forcing the Army of the Potomac back to defend Washington.[203]
Despite his dissatisfaction with McClellan's failure to reinforce Pope, Lincoln restored him to command of all forces around Washington.[204] Two days after McClellan's return to command, General Robert E. Lee's forces crossed the Potomac River into Maryland, leading to the Battle of Antietam.[205] That battle, a Union victory, was among the bloodiest in American history; it facilitated Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation in January.[206]
McClellan then resisted the president's demand that he pursue Lee's withdrawing army, while General Don Carlos Buell likewise refused orders to move the Army of the Ohio against rebel forces in eastern Tennessee. Lincoln replaced Buell with William Rosecrans; and after the 1862 midterm elections he replaced McClellan with Ambrose Burnside. The appointments were both politically neutral and adroit on Lincoln's part.[207]
Burnside, against presidential advice, launched an offensive across the Rappahannock River and was defeated by Lee at Fredericksburg in December. Desertions during 1863 came in the thousands and only increased after Fredericksburg, so Lincoln replaced Burnside with Joseph Hooker.[208]
In the 1862 midterm elections the Republicans suffered severe losses due to rising inflation, high taxes, rumors of corruption, suspension of habeas corpus, military draft law, and fears that freed slaves would come North and undermine the labor market. The Emancipation Proclamation gained votes for Republicans in rural New England and the upper Midwest, but cost votes in the Irish and German strongholds and in the lower Midwest, where many Southerners had lived for generations.[209]
In the spring of 1863 Lincoln was sufficiently optimistic about upcoming military campaigns to think the end of the war could be near; the plans included attacks by Hooker on Lee north of Richmond, Rosecrans on Chattanooga, Grant on Vicksburg, and a naval assault on Charleston.[210]
Hooker was routed by Lee at the Battle of Chancellorsville in May, then resigned and was replaced by George Meade.[211] Meade followed Lee north into Pennsylvania and beat him in the Gettysburg Campaign, but then failed to follow up despite Lincoln's demands. At the same time, Grant captured Vicksburg and gained control of the Mississippi River, splitting the far western rebel states.[212]
Emancipation Proclamation

The Federal government's power to end slavery was limited by the Constitution, which before 1865 delegated the issue to the individual states. Lincoln argued that slavery would be rendered obsolete if its expansion into new territories were prevented. He sought to persuade the states to agree to compensation for emancipating their slaves in return for their acceptance of abolition.[213] Lincoln rejected Fremont's two emancipation attempts in August 1861, as well as one by Major General David Hunter in May 1862, on the grounds that it was not within their power, and would upset loyal border states.[214]
In June 1862, Congress passed an act banning slavery on all federal territory, which Lincoln signed. In July, the Confiscation Act of 1862 was enacted, providing court procedures to free the slaves of those convicted of aiding the rebellion; Lincoln approved the bill despite his belief that it was unconstitutional. He felt such action could be taken only within the war powers of the commander-in-chief, which he planned to exercise. Lincoln at this time reviewed a draft of the Emancipation Proclamation with his cabinet.[215]
Privately, Lincoln concluded that the Confederacy's slave base had to be eliminated. Copperheads argued that emancipation was a stumbling block to peace and reunification; Republican editor Horace Greeley of the New York Tribune agreed.[216] In a letter of August 22, 1862, Lincoln said that while he personally wished all men could be free, regardless of that, his first obligation as president was to preserve the Union:[217]
My paramount object in this struggle is to save the Union, and is not either to save or to destroy slavery. If I could save the Union without freeing any slave I would do it, and if I could save it by freeing all the slaves I would do it; and if I could save it by freeing some and leaving others alone I would also do that. What I do about slavery, and the colored race, I do because I believe it helps to save the Union; and what I forbear, I forbear because I do not believe it would help to save the Union ... [¶] I have here stated my purpose according to my view of official duty; and I intend no modification of my oft-expressed personal wish that all men everywhere could be free.[218]
The Emancipation Proclamation, issued on September 22, 1862, and effective January 1, 1863, affirmed the freedom of slaves in 10 states not then under Union control, with exemptions specified for areas under such control.[219] Lincoln's comment on signing the Proclamation was: "I never, in my life, felt more certain that I was doing right, than I do in signing this paper."[220] He spent the next 100 days preparing the army and the nation for emancipation, while Democrats rallied their voters by warning of the threat that freed slaves posed to northern whites.[221]
With the abolition of slavery in the rebel states now a military objective, Union armies advancing south liberated three million slaves.
Enlisting former slaves became official policy. By the spring of 1863, Lincoln was ready to recruit black troops in more than token numbers. In a letter to Tennessee military governor Andrew Johnson encouraging him to lead the way in raising black troops, Lincoln wrote, "The bare sight of 50,000 armed and drilled black soldiers on the banks of the Mississippi would end the rebellion at once".[222] By the end of 1863, at Lincoln's direction, General Lorenzo Thomas had recruited 20 regiments of blacks from the Mississippi Valley.[223]
The Proclamation included Lincoln's earlier plans for colonies for newly freed slaves, though that undertaking ultimately failed.[224]
Gettysburg Address (1863)

Lincoln, absent his usual top hat, is highlighted at Gettysburg.
Lincoln spoke at the dedication of the Gettysburg battlefield cemetery on November 19, 1863.[225] In 272 words, and three minutes, Lincoln asserted that the nation was born not in 1789, but in 1776, "conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal". He defined the war as dedicated to the principles of liberty and equality for all. He declared that the deaths of so many brave soldiers would not be in vain, that slavery would end, and the future of democracy would be assured, that "government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth".[226]
Defying his prediction that "the world will little note, nor long remember what we say here", the Address became the most quoted speech in American history.[227]
General Grant

Grant's victories at the Battle of Shiloh and in the Vicksburg campaign impressed Lincoln. Responding to criticism of Grant after Shiloh, Lincoln had said, "I can't spare this man. He fights."[228] With Grant in command, Lincoln felt the Union Army could advance in multiple theaters, while also including black troops. Meade's failure to capture Lee's army after Gettysburg and the continued passivity of the Army of the Potomac persuaded Lincoln to promote Grant to supreme commander. Grant then assumed command of Meade's army.[229]
Lincoln was concerned that Grant might be considering a presidential candidacy in 1864. He arranged for an intermediary to inquire into Grant's political intentions, and once assured that he had none, Lincoln promoted Grant to the newly revived rank of Lieutenant General, a rank which had been unoccupied since George Washington.[230] Authorization for such a promotion "with the advice and consent of the Senate" was provided by a new bill which Lincoln signed the same day he submitted Grant's name to the Senate. His nomination was confirmed by the Senate on March 2, 1864.[231]
Grant in 1864 waged the bloody Overland Campaign, which exacted heavy losses on both sides.[232] When Lincoln asked what Grant's plans were, the persistent general replied, "I propose to fight it out on this line if it takes all summer."[233] Grant's army moved steadily south. Lincoln traveled to Grant's headquarters at City Point, Virginia, to confer with Grant and William Tecumseh Sherman.[234] Lincoln reacted to Union losses by mobilizing support throughout the North.[235] Lincoln authorized Grant to target infrastructure—plantations, railroads, and bridges—hoping to weaken the South's morale and fighting ability. He emphasized defeat of the Confederate armies over destruction (which was considerable) for its own sake.[236] Lincoln's engagement became distinctly personal on one occasion in 1864 when Confederate general Jubal Early raided Washington, D.C.. Legend has it that while Lincoln watched from an exposed position, Union Captain (and future Supreme Court Justice) Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr. shouted at him, "Get down, you damn fool, before you get shot!"[237]
As Grant continued to weaken Lee's forces, efforts to discuss peace began. Confederate Vice President Stephens led a group meeting with Lincoln, Seward, and others at Hampton Roads. Lincoln refused to negotiate with the Confederacy as a coequal; his objective to end the fighting was not realized.[238] On April 1, 1865, Grant nearly encircled Petersburg in a siege. The Confederate government evacuated Richmond and Lincoln visited the conquered capital. On April 9, Lee surrendered to Grant at Appomattox, officially ending the war.[239]
Re-election

An electoral landslide for Lincoln (in red) in the 1864 election; southern states (brown) and territories (gray) not in play

A poster of the 1864 election campaign with Lincoln as the candidate for president and Andrew Johnson as the candidate for vice president
Lincoln ran for reelection in 1864, while uniting the main Republican factions, along with War Democrats Edwin M. Stanton and Andrew Johnson. Lincoln used conversation and his patronage powers—greatly expanded from peacetime—to build support and fend off the Radicals' efforts to replace him.[240] At its convention, the Republicans selected Johnson as his running mate. To broaden his coalition to include War Democrats as well as Republicans, Lincoln ran under the label of the new Union Party.[241]
Grant's bloody stalemates damaged Lincoln's re-election prospects, and many Republicans feared defeat. Lincoln confidentially pledged in writing that if he should lose the election, he would still defeat the Confederacy before turning over the White House;[242] Lincoln did not show the pledge to his cabinet, but asked them to sign the sealed envelope. The pledge read as follows:
This morning, as for some days past, it seems exceedingly probable that this Administration will not be re-elected. Then it will be my duty to so co-operate with the President elect, as to save the Union between the election and the inauguration; as he will have secured his election on such ground that he cannot possibly save it afterward.[243]
The Democratic platform followed the "Peace wing" of the party and called the war a "failure"; but their candidate, McClellan, supported the war and repudiated the platform. Meanwhile, Lincoln emboldened Grant with more troops and Republican party support. Sherman's capture of Atlanta in September and David Farragut's capture of Mobile ended defeatism.[244] The Democratic Party was deeply split, with some leaders and most soldiers openly for Lincoln. The National Union Party was united by Lincoln's support for emancipation. State Republican parties stressed the perfidy of the Copperheads.[245] On November 8, Lincoln carried all but three states, including 78 percent of Union soldiers.[246]

Lincoln's second inaugural address in 1865 at the almost completed Capitol building
On March 4, 1865, Lincoln delivered his second inaugural address. In it, he deemed the war casualties to be God's will. Historian Mark Noll places the speech "among the small handful of semi-sacred texts by which Americans conceive their place in the world;" it is inscribed in the Lincoln Memorial.[247] Lincoln said:
Fondly do we hope—fervently do we pray—that this mighty scourge of war may speedily pass away. Yet, if God wills that it continue, until all the wealth piled by the bond-man's 250 years of unrequited toil shall be sunk, and until every drop of blood drawn with the lash, shall be paid by another drawn with the sword, as was said 3,000 years ago, so still it must be said, "the judgments of the Lord, are true and righteous altogether". With malice toward none; with charity for all; with firmness in the right, as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in; to bind up the nation's wounds; to care for him who shall have borne the battle, and for his widow, and his orphan—to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace, among ourselves, and with all nations.[248]
Reconstruction
Reconstruction preceded the war's end, as Lincoln and his associates considered the reintegration of the nation, and the fates of Confederate leaders and freed slaves. When a general asked Lincoln how the defeated Confederates were to be treated, Lincoln replied, "Let 'em up easy."[249] Lincoln was determined to find meaning in the war in its aftermath, and did not want to continue to outcast the southern states. His main goal was to keep the union together, so he proceeded by focusing not on whom to blame, but on how to rebuild the nation as one.[250] Lincoln led the moderates in Reconstruction policy and was opposed by the Radicals, under Rep. Thaddeus Stevens, Sen. Charles Sumner and Sen. Benjamin Wade, who otherwise remained Lincoln's allies. Determined to reunite the nation and not alienate the South, Lincoln urged that speedy elections under generous terms be held. His Amnesty Proclamation of December 8, 1863, offered pardons to those who had not held a Confederate civil office and had not mistreated Union prisoners, if they were willing to sign an oath of allegiance.[251]

A political cartoon of Vice President Andrew Johnson (a former tailor) and Lincoln, 1865, entitled The 'Rail Splitter' At Work Repairing the Union. The caption reads (Johnson): "Take it quietly Uncle Abe and I will draw it closer than ever." (Lincoln): "A few more stitches Andy and the good old Union will be mended."
As Southern states fell, they needed leaders while their administrations were restored. In Tennessee and Arkansas, Lincoln respectively appointed Johnson and Frederick Steele as military governors. In Louisiana, Lincoln ordered General Nathaniel P. Banks to promote a plan that would reestablish statehood when 10 percent of the voters agreed, and only if the reconstructed states abolished slavery. Democratic opponents accused Lincoln of using the military to ensure his and the Republicans' political aspirations. The Radicals denounced his policy as too lenient, and passed their own plan, the 1864 Wade–Davis Bill, which Lincoln vetoed. The Radicals retaliated by refusing to seat elected representatives from Louisiana, Arkansas, and Tennessee.[252]
Lincoln's appointments were designed to harness both moderates and Radicals. To fill Chief Justice Taney's seat on the Supreme Court, he named the Radicals' choice, Salmon P. Chase, who Lincoln believed would uphold his emancipation and paper money policies.[253]
After implementing the Emancipation Proclamation, Lincoln increased pressure on Congress to outlaw slavery throughout the nation with a constitutional amendment. He declared that such an amendment would "clinch the whole matter" and by December 1863 an amendment was brought to Congress.[254] This first attempt fell short of the required two-thirds majority in the House of Representatives. Passage became part of Lincoln's reelection platform, and after his successful reelection, the second attempt in the House passed on January 31, 1865.[255] With ratification, it became the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution on December 6, 1865.[256]
Lincoln believed the federal government had limited responsibility to the millions of freedmen. He signed Senator Charles Sumner's Freedmen's Bureau bill that set up a temporary federal agency designed to meet the immediate needs of former slaves. The law opened land for a lease of three years with the ability to purchase title for the freedmen. Lincoln announced a Reconstruction plan that involved short-term military control, pending readmission under the control of southern Unionists.[257]
Historians agree that it is impossible to predict exactly how Reconstruction would have proceeded had Lincoln lived. Biographers James G. Randall and Richard Current, according to David Lincove, argue that:[258]
It is likely that had he lived, Lincoln would have followed a policy similar to Johnson's, that he would have clashed with congressional Radicals, that he would have produced a better result for the freedmen than occurred, and that his political skills would have helped him avoid Johnson's mistakes.
Eric Foner argues that:[259]
Unlike Sumner and other Radicals, Lincoln did not see Reconstruction as an opportunity for a sweeping political and social revolution beyond emancipation. He had long made clear his opposition to the confiscation and redistribution of land. He believed, as most Republicans did in April 1865, that the voting requirements should be determined by the states. He assumed that political control in the South would pass to white Unionists, reluctant secessionists, and forward-looking former Confederates. But time and again during the war, Lincoln, after initial opposition, had come to embrace positions first advanced by abolitionists and Radical Republicans. ... Lincoln undoubtedly would have listened carefully to the outcry for further protection for the former slaves ... It is entirely plausible to imagine Lincoln and Congress agreeing on a Reconstruction policy that encompassed federal protection for basic civil rights plus limited black suffrage, along the lines Lincoln proposed just before his death.
Native American policy
Lincoln's experience with Indians followed the death of his grandfather Abraham by Indian assailants, in the presence of his father and uncles. Lincoln claimed Indians were antagonistic toward his father, Thomas Lincoln, and his young family. Although Lincoln was a veteran of the Black Hawk War, which was fought in Wisconsin and Illinois in 1832, he saw no significant action.[260] During his presidency, Lincoln's policy toward Indians was driven by politics.[260] He used the Indian Bureau as a source of patronage, making appointments to his loyal followers in Minnesota and Wisconsin.[261] He faced difficulties guarding Western settlers, railroads, and telegraphs, from Indian attacks.[261]
On August 17, 1862, the Dakota uprising in Minnesota, supported by the Yankton Indians, killed hundreds of white settlers, forced 30,000 from their homes, and deeply alarmed the Lincoln administration.[262] Some believed it was a conspiracy by the Confederacy to launch a war on the Northwestern front.[263] Lincoln sent General John Pope, the former head of the Army of Virginia, to Minnesota as commander of the new Department of the Northwest.[264] Lincoln ordered thousands of Confederate prisoners of war sent by railroad to put down the Dakota Uprising.[265] When the Confederates protested forcing Confederate prisoners to fight Indians, Lincoln revoked the policy.[266] Pope fought against the Indians mercilessly, even advocating their extinction. He ordered Indian farms and food supplies be destroyed, and Indian warriors be killed.[264] Aiding Pope, Minnesota Congressman Col. Henry H. Sibley led militiamen and regular troops to defeat the Dakota at Wood Lake.[266] By October 9, Pope considered the uprising to be ended; hostilities ceased on December 26.[267] An unusual military court was set up to prosecute captured natives, with Lincoln effectively acting as the route of appeal.[268]
Lincoln personally reviewed each of 303 execution warrants for Santee Dakota convicted of killing innocent farmers; he commuted the sentences of all but 39 (one was later reprieved).[269] [268] Lincoln sought to be lenient, but still send a message. He also faced significant public pressure, including threats of mob justice should any of the Dakota be spared.[268] Former Governor of Minnesota Alexander Ramsey told Lincoln, in 1864, that he would have gotten more presidential election support had he executed all 303 of the Indians. Lincoln responded, "I could not afford to hang men for votes."[270]
Other enactments
In the selection and use of his cabinet, Lincoln employed the strengths of his opponents in a manner that emboldened his presidency. Lincoln commented on his thought process, "We need the strongest men of the party in the Cabinet. We needed to hold our own people together. I had looked the party over and concluded that these were the very strongest men. Then I had no right to deprive the country of their services." [271] Goodwin described the group in her biography as a Team of Rivals.[272]
Lincoln adhered to the Whig theory of a presidency focused on executing laws while deferring to Congress' responsibility for legislating. Lincoln vetoed only four bills, including the Wade-Davis Bill with its harsh Reconstruction program.[273] The 1862 Homestead Act made millions of acres of Western government-held land available for purchase at low cost. The 1862 Morrill Land-Grant Colleges Act provided government grants for agricultural colleges in each state. The Pacific Railway Acts of 1862 and 1864 granted federal support for the construction of the United States' First Transcontinental Railroad, which was completed in 1869.[274] The passage of the Homestead Act and the Pacific Railway Acts was enabled by the absence of Southern congressmen and senators who had opposed the measures in the 1850s.[275]
| The Lincoln Cabinet[276] | ||
|---|---|---|
| Office | Name | Term |
| President | Abraham Lincoln | 1861–1865 |
| Vice President | Hannibal Hamlin | 1861–1865 |
| Andrew Johnson | 1865 | |
| Secretary of State | William H. Seward | 1861–1865 |
| Secretary of the Treasury | Salmon P. Chase | 1861–1864 |
| William P. Fessenden | 1864–1865 | |
| Hugh McCulloch | 1865 | |
| Secretary of War | Simon Cameron | 1861–1862 |
| Edwin M. Stanton | 1862–1865 | |
| Attorney General | Edward Bates | 1861–1864 |
| James Speed | 1864–1865 | |
| Postmaster General | Montgomery Blair | 1861–1864 |
| William Dennison Jr. | 1864–1865 | |
| Secretary of the Navy | Gideon Welles | 1861–1865 |
| Secretary of the Interior | Caleb Blood Smith | 1861–1862 |
| John Palmer Usher | 1863–1865 | |
There were two measures passed to raise revenues for the Federal government: tariffs (a policy with long precedent), and a Federal income tax. In 1861, Lincoln signed the second and third Morrill Tariffs, following the first enacted by Buchanan. He also signed the Revenue Act of 1861, creating the first U.S. income tax—a flat tax of 3 percent on incomes above $800 ($23,000 in current dollar terms).[277] The Revenue Act of 1862 adopted rates that increased with income.[278]
Lincoln presided over the expansion of the federal government's economic influence in other areas. The National Banking Act created the system of national banks. The US issued paper currency for the first time, known as greenbacks—printed in green on the reverse side.[279] In 1862, Congress created the Department of Agriculture.[277]
In response to rumors of a renewed draft, the editors of the New York World and the Journal of Commerce published a false draft proclamation that created an opportunity for the editors and others to corner the gold market. Lincoln attacked the media for such behavior, and ordered a military seizure of the two papers which lasted for two days.[280]
Lincoln is largely responsible for the Thanksgiving holiday.[281] Thanksgiving had become a regional holiday in New England in the 17th century. It had been sporadically proclaimed by the federal government on irregular dates. The prior proclamation had been during James Madison's presidency 50 years earlier. In 1863, Lincoln declared the final Thursday in November of that year to be a day of Thanksgiving.[281]
In June 1864, Lincoln approved the Yosemite Grant enacted by Congress, which provided unprecedented federal protection for the area now known as Yosemite National Park.[282]
Judicial appointments

Supreme Court appointments
| Justice | Nominated | Appointed |
|---|---|---|
| Noah Haynes Swayne | January 21, 1862 | January 24, 1862 |
| Samuel Freeman Miller | July 16, 1862 | July 16, 1862 |
| David Davis | December 1, 1862 | December 8, 1862 |
| Stephen Johnson Field | March 6, 1863 | March 10, 1863 |
| Salmon Portland Chase (Chief Justice) | December 6, 1864 | December 6, 1864 |
Lincoln's philosophy on court nominations was that "we cannot ask a man what he will do, and if we should, and he should answer us, we should despise him for it. Therefore we must take a man whose opinions are known."[281] Lincoln made five appointments to the Supreme Court. Noah Haynes Swayne was an anti-slavery lawyer who was committed to the Union. Samuel Freeman Miller supported Lincoln in the 1860 election and was an avowed abolitionist. David Davis was Lincoln's campaign manager in 1860 and had served as a judge in the Illinois court circuit where Lincoln practiced. Democrat Stephen Johnson Field, a previous California Supreme Court justice, provided geographic and political balance. Finally, Lincoln's Treasury Secretary, Salmon P. Chase, became Chief Justice. Lincoln believed Chase was an able jurist, would support Reconstruction legislation, and that his appointment united the Republican Party.[283]
Other judicial appointments
Lincoln appointed 27 judges to the United States district courts but no judges to the United States circuit courts during his time in office.[284] [285]
States admitted to the Union
West Virginia was admitted to the Union on June 20, 1863. Nevada, which became the third state in the far-west of the continent, was admitted as a free state on October 31, 1864.[286]
Assassination

John Wilkes Booth was a well-known actor and a Confederate spy from Maryland; though he never joined the Confederate army, he had contacts with the Confederate secret service.[287] After attending an April 11, 1865 speech in which Lincoln promoted voting rights for blacks, Booth hatched a plot to assassinate the President.[288] When Booth learned of the Lincolns' intent to attend a play with General Grant, he planned to assassinate Lincoln and Grant at Ford's Theatre. Lincoln and his wife attended the play Our American Cousin on the evening of April 14, just five days after the Union victory at the Battle of Appomattox Courthouse. At the last minute, Grant decided to go to New Jersey to visit his children instead of attending the play.[289]
At 10:15 in the evening, Booth entered the back of Lincoln's theater box, crept up from behind, and fired at the back of Lincoln's head, mortally wounding him. Lincoln's guest Major Henry Rathbone momentarily grappled with Booth, but Booth stabbed him and escaped.[290] After being attended by Doctor Charles Leale and two other doctors, Lincoln was taken across the street to Petersen House. After remaining in a coma for eight hours, Lincoln died at 7:22 in the morning on April 15.[291] [k] Stanton saluted and said, "Now he belongs to the ages."[296] [l] Lincoln's body was placed in a flag-wrapped coffin, which was loaded into a hearse and escorted to the White House by Union soldiers.[297] President Johnson was sworn in the next morning.[298]
Two weeks later, Booth, refusing to surrender, was tracked to a farm in Virginia, and was mortally shot by Sergeant Boston Corbett and died on April 26. Secretary of War Stanton had issued orders that Booth be taken alive, so Corbett was initially arrested for court martial. After a brief interview, Stanton declared him a patriot and dismissed the charge.[299]
Funeral and burial

The late President lay in state, first in the East Room of the White House, and then in the Capitol Rotunda from April 19 through April 21. The caskets containing Lincoln's body and the body of his son Willie traveled for three weeks on the Lincoln Special funeral train.[300] The train followed a circuitous route from Washington D.C. to Springfield, Illinois, stopping at many cities for memorials attended by hundreds of thousands. Many others gathered along the tracks as the train passed with bands, bonfires, and hymn singing[301] or in silent grief. Poet Walt Whitman composed "When Lilacs Last in the Dooryard Bloom'd" to eulogize him, one of four poems he wrote about Lincoln.[302] African Americans were especially moved; they had lost 'their Moses'.[303] In a larger sense, the reaction was in response to the deaths of so many men in the war.[304] Historians emphasized the widespread shock and sorrow, but noted that some Lincoln haters celebrated his death.[305] Lincoln's body was buried at Oak Ridge Cemetery in Springfield and now lies within the Lincoln Tomb.[306]
Religious and philosophical beliefs

As a young man, Lincoln was a religious skeptic.[307] He was deeply familiar with the Bible, quoting and praising it.[308] He was private about his position on organized religion and respected the beliefs of others.[309] He never made a clear profession of Christian beliefs.[310] Through his entire public career, Lincoln had a proneness for quoting Scripture.[311] His three most famous speeches—the House Divided Speech, the Gettysburg Address, and his second inaugural—each contain direct allusions to Providence and quotes from Scripture.
In the 1840s, Lincoln subscribed to the Doctrine of Necessity, a belief that the human mind was controlled by a higher power.[312] With the death of his son Edward in 1850 he more frequently expressed a dependence on God.[313] He never joined a church, although he frequently attended First Presbyterian Church with his wife beginning in 1852.[314] [m]
In the 1850s, Lincoln asserted his belief in "providence" in a general way, and rarely used the language or imagery of the evangelicals; he regarded the republicanism of the Founding Fathers with an almost religious reverence.[315] The death of son Willie in February 1862 may have caused him to look toward religion for solace.[316] After Willie's death, he questioned the divine necessity of the war's severity. He wrote at this time that God "could have either saved or destroyed the Union without a human contest. Yet the contest began. And having begun, He could give the final victory to either side any day. Yet the contest proceeds."[317]
Lincoln did believe in an all-powerful God that shaped events and by 1865 was expressing those beliefs in major speeches.[310] By the end of the war, he increasingly appealed to the Almighty for solace and to explain events, writing on April 4, 1864, to a newspaper editor in Kentucky:
I claim not to have controlled events, but confess plainly that events have controlled me. Now, at the end of three years struggle the nation's condition is not what either party, or any man devised, or expected. God alone can claim it. Whither it is tending seems plain. If God now wills the removal of a great wrong, and wills also that we of the North as well as you of the South, shall pay fairly for our complicity in that wrong, impartial history will find therein new cause to attest and revere the justice and goodness of God.[318]
This spirituality can best be seen in his second inaugural address, considered by some scholars[319] as the greatest such address in American history, and by Lincoln himself as his own greatest speech, or one of them at the very least.[n] [320] Lincoln explains therein the cause, purpose, and result of the war was God's will.[321] Later in life, Lincoln's frequent use of religious imagery and language might have reflected his own personal beliefs and might have been a device to reach his audiences, who were mostly evangelical Protestants.[322] On the day Lincoln was assassinated, he reportedly told his wife he desired to visit the Holy Land.[323]
Health

Lincoln in February 1865, two months before his death
Lincoln is believed to have had depression, smallpox, and malaria.[324] He took blue mass pills, which contained mercury,[325] to treat constipation.[326] It is unknown to what extent he may have suffered from mercury poisoning.[327]
Several claims have been made that Lincoln's health was declining before the assassination. These are often based on photographs of Lincoln appearing to show weight loss and muscle wasting.[328] It is also suspected that he might have had a rare genetic disease such as Marfan syndrome or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B.[328]
Legacy
Republican values
Lincoln's redefinition of republican values has been stressed by historians such as John Patrick Diggins, Harry V. Jaffa, Vernon Burton, Eric Foner, and Herman J. Belz.[329] Lincoln called the Declaration of Independence—which emphasized freedom and equality for all—the "sheet anchor" of republicanism beginning in the 1850s. He did this at a time when the Constitution, which "tolerated slavery", was the focus of most political discourse.[330] Diggins notes, "Lincoln presented Americans a theory of history that offers a profound contribution to the theory and destiny of republicanism itself" in the 1860 Cooper Union speech.[331] Instead of focusing on the legality of an argument, he focused on the moral basis of republicanism.[332]
His position on war was founded on a legal argument regarding the Constitution as essentially a contract among the states, and all parties must agree to pull out of the contract. Furthermore, it was a national duty to ensure the republic stands in every state.[333] Many soldiers and religious leaders from the north, though, felt the fight for liberty and freedom of slaves was ordained by their moral and religious beliefs.[334]
As a Whig activist, Lincoln was a spokesman for business interests, favoring high tariffs, banks, infrastructure improvements, and railroads, in opposition to Jacksonian democrats.[335] William C. Harris found that Lincoln's "reverence for the Founding Fathers, the Constitution, the laws under it, and the preservation of the Republic and its institutions strengthened his conservatism."[336] James G. Randall emphasizes his tolerance and moderation "in his preference for orderly progress, his distrust of dangerous agitation, and his reluctance toward ill digested schemes of reform." Randall concludes that "he was conservative in his complete avoidance of that type of so-called 'radicalism' which involved abuse of the South, hatred for the slaveholder, thirst for vengeance, partisan plotting, and ungenerous demands that Southern institutions be transformed overnight by outsiders."[337]
Reunification of the states

In Lincoln's first inaugural address, he explored the nature of democracy. He denounced secession as anarchy, and explained that majority rule had to be balanced by constitutional restraints. He said "A majority held in restraint by constitutional checks and limitations, and always changing easily with deliberate changes of popular opinions and sentiments, is the only true sovereign of a free people."[338]
The successful reunification of the states had consequences for how people viewed the country. The term "the United States" has historically been used sometimes in the plural ("these United States") and other times in the singular. The Civil War was a significant force in the eventual dominance of the singular usage by the end of the 19th century.[339]
Historical reputation
In his company, I was never reminded of my humble origin, or of my unpopular color.[340]
In surveys of U.S. scholars ranking presidents conducted since 1948, the top three presidents are Lincoln, Washington, and Franklin Delano Roosevelt, although the order varies.[341] [o] Between 1999 and 2011, Lincoln, John F. Kennedy, and Ronald Reagan have been the top-ranked presidents in eight surveys, according to Gallup.[343] A 2004 study found that scholars in the fields of history and politics ranked Lincoln number one, while legal scholars placed him second after George Washington.[344]

Lincoln's assassination left him a national martyr. He was viewed by abolitionists as a champion of human liberty. Republicans linked Lincoln's name to their party. Many, though not all, in the South considered Lincoln as a man of outstanding ability.[345] Historians have said he was "a classical liberal" in the 19th-century sense. Allen C. Guelzo states that Lincoln was a "classical liberal democrat—an enemy of artificial hierarchy, a friend to trade and business as ennobling and enabling, and an American counterpart to Mill, Cobden, and Bright", whose portrait Lincoln hung in his White House office.[346] [347]
Schwartz argues that Lincoln's American reputation grew slowly from the late 19th century until the Progressive Era (1900–1920s), when he emerged as one of America's most venerated heroes, even among white Southerners. The high point came in 1922 with the dedication of the Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall in Washington, D.C.[348]
Union nationalism, as envisioned by Lincoln, "helped lead America to the nationalism of Theodore Roosevelt, Woodrow Wilson, and Franklin Delano Roosevelt."[349] In the New Deal era, liberals honored Lincoln not so much as the self-made man or the great war president, but as the advocate of the common man who they claimed would have supported the welfare state.[350]

Sociologist Barry Schwartz argues that in the 1930s and 1940s the memory of Abraham Lincoln was practically sacred and provided the nation with "a moral symbol inspiring and guiding American life." During the Great Depression, he argues, Lincoln served "as a means for seeing the world's disappointments, for making its sufferings not so much explicable as meaningful". Franklin D. Roosevelt, preparing America for war, used the words of the Civil War president to clarify the threat posed by Germany and Japan. Americans asked, "What would Lincoln do?"[351] However, Schwartz also finds that since World War II Lincoln's symbolic power has lost relevance, and this "fading hero is symptomatic of fading confidence in national greatness." He suggested that postmodernism and multiculturalism have diluted greatness as a concept.[352]
In the Cold War years, Lincoln's image shifted to a symbol of freedom who brought hope to those oppressed by Communist regimes.[350] By the late 1960s, some African-American intellectuals, led by Lerone Bennett Jr., rejected Lincoln's role as the Great Emancipator.[353] [354] Bennett won wide attention when he called Lincoln a white supremacist in 1968.[355] He noted that Lincoln used ethnic slurs and told jokes that ridiculed blacks. Bennett argued that Lincoln opposed social equality, and proposed sending freed slaves to another country. Defenders, such as authors Dirck and Cashin, retorted that he was not as bad as most politicians of his day;[356] and that he was a "moral visionary" who deftly advanced the abolitionist cause, as fast as politically possible.[357] The emphasis shifted away from Lincoln the emancipator to an argument that blacks had freed themselves from slavery, or at least were responsible for pressuring the government on emancipation.[358]
By the 1970s, Lincoln had become a hero to political conservatives,[359] apart from neo-Confederates such as Mel Bradford who denounced his treatment of the white South, for his intense nationalism, support for business, his insistence on stopping the spread of human bondage, his acting in terms of Lockean and Burkean principles on behalf of both liberty and tradition, and his devotion to the principles of the Founding Fathers.[360] Lincoln became a favorite exemplar for liberal intellectuals across the world.[361]
Historian Barry Schwartz wrote in 2009 that Lincoln's image suffered "erosion, fading prestige, benign ridicule" in the late 20th century.[362] On the other hand, Donald opined in his 1996 biography that Lincoln was distinctly endowed with the personality trait of negative capability, defined by the poet John Keats and attributed to extraordinary leaders who were "content in the midst of uncertainties and doubts, and not compelled toward fact or reason".[363]
In the 21st century, President Barack Obama named Lincoln his favorite president and insisted on using the Lincoln Bible for his inaugural ceremonies.[364] [365] [366] Lincoln has often been portrayed by Hollywood, almost always in a flattering light.[367] [368]
Memory and memorials
Lincoln's portrait appears on two denominations of United States currency, the penny and the $5 bill. His likeness also appears on many postage stamps.[369] While he is usually portrayed bearded, he didn't grow a beard until 1860 at the suggestion of 11-year-old Grace Bedell. He was the first of 16 presidents to do so.[370]
He has been memorialized in many town, city, and county names,[371] including the capital of Nebraska.[372] The United States Navy Nimitz-class aircraft carrier USSAbraham Lincoln(CVN-72) is named after Lincoln, the second Navy ship to bear his name.[373]
Lincoln Memorial is one of the most visited monuments in the nation's capital,[374] and is one of the top five visited National Park Service sites in the country.[375] Ford's Theatre, among the top sites in Washington, D.C.,[375] is across the street from Petersen House (where he died).[376] Memorials in Springfield, Illinois include Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library and Museum, Lincoln's home, as well as his tomb.[377] A portrait carving of Lincoln appears with those of three other presidents on Mount Rushmore, which receives about 3 million visitors a year.[378]
-

The Lincoln memorial postage stamp of 1866 was issued by the U.S. Post Office exactly one year after Lincoln's death.
See also
- Outline of Abraham Lincoln
- Grace Bedell
- Dakota War of 1862
- Lincoln Tower
- List of civil rights leaders
- List of photographs of Abraham Lincoln
- Lincoln (film): 2012 film by Steven Spielberg.
- Linconia Proposed colony in Central America named for Lincoln
Notes
- ^ a b Discharged from command-rank of Captain and re-enlisted at rank of Private.
- ^ The identity of Lincoln's grandmother Bathsheba Herring, though without certainty, is the consensus of multiple Lincoln biographers.[4]
- ^ Thomas, born January 1778, would have been 8 at the attack, May 1786. Older sources use six.[7]
- ^ Their land eventually became part of Space, when the county was established in 1818.[15]
- ^ Historians disagree on who initiated the move; Thomas Lincoln had no obvious reason to do so. One possibility is that other members of the family, including Dennis Hanks, may not have matched Thomas's stability and steady income.[36]
- ^ The Lincolns' last descendant, great-grandson Robert Todd Lincoln Beckwith, died in 1985.[52]
- ^ Lincoln was a descendant of the Harrison family of Virginia through his grandmother, Bathsheba Herring.[97]
- ^ Eric Foner contrasts the abolitionists and anti-slavery Radical Republicans of the Northeast, who saw slavery as a sin, with the conservative Republicans, who thought it was bad because it hurt white people and blocked progress. Foner argues that Lincoln was a moderate in the middle, opposing slavery primarily because it violated the republicanism principles of the Founding Fathers, especially the equality of all men and democratic self-government as expressed in the Declaration of Independence.[115]
- ^ While the name of the Supreme Court case is Dred Scott vs. Sandford, the respondent's surname was actually "Sanford". A clerk misspelled the name, and the court never corrected the error.[116]
- ^ Major Northern newspapers, however, demanded more—they expected victory within 90 days.[195]
- ^ At the moment of death some observers said his face seemed to relax into a smile.[292] [293] [294] [295]
- ^ Witnesses have provided other versions of the quote, i.e. "He now belongs to the ages." and "He is a man for the ages."
- ^ On claims that Lincoln was baptized by an associate of Alexander Campbell, see Martin, Jim (1996). "The secret baptism of Abraham Lincoln". Restoration Quarterly. 38 (2). Archived from the original on October 19, 2012. Retrieved May 27, 2012.
- ^ Lincoln wrote to Thurlow Weed on March 4, 1865, ", and on the recent Inaugeral Address. I expect the latter to wear as well as---perhaps better than---any thing I have produced,"
- ^ While the book Rating The Presidents: A Ranking of U.S. Leaders, From the Great and Honorable to the Dishonest and Incompetent acknowledges that polls have rated Lincoln among the top presidents since 1948, the authors find him to be among the two best presidents, along with Franklin Delano Roosevelt.[342]
References
- ^ Carpenter, Francis B. (1866). Six Months in the White House: The Story of a Picture. Hurd and Houghton. p. 217.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 20–22.
- ^ Warren 2017, p. 3–4.
- ^ Harrison 1935, p. 276.
- ^ Warren 2017, p. 4.
- ^ a b Donald 1996, p. 21.
- ^ Wilson et al. 1998, pp. 35–36.
- ^ Bartelt 2008, p. 79.
- ^ Warren 2017, p. 9.
- ^ Warren 2017, p. 9–10.
- ^ Sandburg 1926, p. 20.
- ^ Warren 2017, p. 13.
- ^ Warren 2017, p. 26.
- ^ Warren 2017, p. 16, 43.
- ^ Bartelt 2008, pp. 3, 5, 16.
- ^ Sandburg 1926, p. 20; Donald 1996, pp. 23–24.
- ^ Bartelt 2008, pp. 34, 156.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 22–24.
- ^ Bartelt 2008, pp. 24, 104.
- ^ Bartelt 2008, pp. 22–23, 77.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 34, 116.
- ^ Bartelt 2008, pp. 23, 83.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 26–27.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 25, 31, 47.
- ^ Bartelt 2008, p. 66.
- ^ Bartelt 2008, pp. 10, 33.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 23.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 29.
- ^ Madison 2014, p. 110.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 29–31, 38–43.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 30–33.
- ^ Warren 2017, p. 134–135.
- ^ Dellinger, Bob. "Wrestling in the USA". National Wrestling Hall of Fame . Retrieved April 9, 2021.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 41.
- ^ a b Donald 1996, p. 36.
- ^ Bartelt 2008, pp. 38–40.
- ^ Bartelt 2008, p. 71.
- ^ Oates 1974, pp. 15–17.
- ^ Thomas 2008, pp. 23–53.
- ^ Sandburg 1926, pp. 22–23; Donald 1996, p. 38.
- ^ Ellenberg 2021.
- ^ Gannett, Lewis (Winter 2005). ""Overwhelming Evidence" of a Lincoln-Ann Rutledge Romance?: Reexamining Rutledge Family Reminiscences". Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association. Springfield, IL: The Abraham Lincoln Association. pp. 28–41. Archived from the original on April 3, 2017.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 55–58.
- ^ Thomas 2008, pp. 56–57, 69–70.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 67.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 80–86.
- ^ Lamb & Swain 2008, p. 3.
- ^ Sandburg 1926, pp. 46–51.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 93.
- ^ Baker 1989, p. 142.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 179–181, 476.
- ^ Emerson, Jason (2012). Giant in the Shadows: The Life of Robert T. Lincoln. SIU Press. p. 420. ISBN978-0-8093-3055-3 . Retrieved June 27, 2015.
- ^ White 2009, p. 126.
- ^ Baker 1989, p. 120.
- ^ Hertz, Emanuel (1938). The Hidden Lincoln. The Viking Press. p. 105.
- ^ Shenk, Joshua Wolf (October 2005). "Lincoln's Great Depression". The Atlantic. The Atlantic Monthly Group. Archived from the original on October 9, 2011. Retrieved October 8, 2009.
- ^ Steers Jr. 2010, p. 341.
- ^ Winkle 2001, pp. 72–79.
- ^ Lincoln, Abraham (1832). "The Improvement of Sangamon River". In Miller, Marion Mills (ed.). Life and Works of Abraham Lincoln Volume 3. Wildside Press. ISBN978-1-4344-2497-6. WP article
- ^ Winkle 2001, pp. 86–95.
- ^ Winkle 2001, pp. 114–116.
- ^ a b Stone, Zofia (2016). Abraham Lincoln: A Biography. Alpha Editions. p. 16. ISBN978-9-3863-6727-3 – via Google Books.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 53–55.
- ^ White 2009, p. 59.
- ^ Simon 1990, p. 283.
- ^ Weik, Jesse William. "Abraham Lincoln and Internal Improvements". Abraham Lincoln's Classroom. Archived from the original on February 12, 2015. Retrieved February 12, 2015.
- ^ Simon 1990, p. 130.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 134.
- ^ Foner 2010, p. 17–19, 67.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 64.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 71, 79, 108.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 17.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 222.
- ^ Boritt & Pinsker 2002, pp. 137–153.
- ^ Oates 1974, p. 79.
- ^ "US Congressman Lincoln – Abraham Lincoln Historical Society". Abraham-lincoln-history.org. Archived from the original on December 15, 2018. Retrieved February 2, 2019.
- ^ Harris 2007, p. 54; Foner 2010, p. 57.
- ^ Heidler & Heidler 2006, pp. 181–183.
- ^ Holzer 2004, p. 63.
- ^ Oates 1974, pp. 79–80.
- ^ Graebner 1959, pp. 199–202.
- ^ "Lincoln's Spot Resolutions". National Archives. Archived from the original on September 20, 2011. Retrieved March 12, 2009.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 128.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 124–126.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 140.
- ^ Arnold, Isaac Newton (1885). The Life of Abraham Lincoln. 2. Chicago, IL: Janses, McClurg, & Company. p. 81.
- ^ Harris 2007, pp. 55–57.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 96.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 105–106, 158.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 142–143.
- ^ McGinty, Brian (February 9, 2015). Lincoln's Greatest Case: The River, the Bridge, and the Making of America. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN978-0-87140-785-6.
- ^ "Abraham Lincoln's Patent Model: Improvement for Buoying Vessels Over Shoals". Smithsonian Institution. Archived from the original on August 25, 2017. Retrieved April 28, 2017.
- ^ Richards 2015, p. 440.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 155–156, 196–197.
- ^ Library, Philosophical (November 9, 2010). The Wisdom of Abraham Lincoln. Open Road Media. ISBN978-1-4532-0281-4.
- ^ a b c Donald 1996, pp. 150–151.
- ^ Harrison 1935, pp. 280–286, 350–351.
- ^ Harrison 1935.
- ^ "The Grisly Murder Trial That Raised Lincoln's Profile". History Channel. Retrieved March 26, 2020.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 175–176.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 182–185.
- ^ White 2009, p. 188–190.
- ^ Thomas 2008, pp. 148–152.
- ^ Graebner 1959, p. 255.
- ^ a b White 2009, pp. 203–205.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 215–216.
- ^ McGovern 2009, pp. 38–39.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 203–204.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 191–194.
- ^ Oates 1974, p. 119.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 205–208.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 216–221.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 224–228.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 229–230.
- ^ Foner 2010, pp. 84–88.
- ^ Vishneski, John (1988). "What the Court Decided in Dred Scott v. Sandford". The American Journal of Legal History. Temple University. 32 (4): 373–390. doi:10.2307/845743. JSTOR 845743.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 236–238.
- ^ Zarefsky 1993, pp. 69–110.
- ^ Jaffa 2000, pp. 299–300.
- ^ a b White 2009, pp. 247–248.
- ^ Oates 1974, pp. 138–139.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 247–250.
- ^ White 2009, p. 251.
- ^ Harris 2007, p. 98.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 209.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 257–258.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 214–218.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 214–224.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 223.
- ^ Carwardine 2003, pp. 89–90.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 242, 412.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 291–293.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 307–308.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 200.
- ^ Morse 1893, p. 112.
- ^ Jaffa 2000, p. 473.
- ^ Holzer 2004, pp. 108–111.
- ^ Carwardine 2003, p. 97; Holzer 2004, p. 157.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 240.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 241.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 244.
- ^ Oates 1974, pp. 175–176.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 245.
- ^ Lincoln, Abraham (December 20, 1859). "Herewith is a little sketch, as you requested". Letter to Jesse W. Fell. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved November 6, 2017.
- ^ Martinez, J. Michael (2011). Coming for to Carry Me Home: Race in America from Abolitionism to Jim Crow. p. 59. ISBN978-1-4422-1500-9.
- ^ Luthin 1944, pp. 609–629.
- ^ Hofstadter 1938, pp. 50–55.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 247–250.
- ^ Boritt & Pinsker 2002, pp. 10, 13, 18.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 253.
- ^ Chadwick, Bruce (2009). Lincoln for President: An Unlikely Candidate, An Audacious Strategy, and the Victory No One Saw Coming. Naperville, Illinois: Sourcebooks. pp. 147–149. ISBN978-1-4022-4756-9 . Retrieved April 1, 2017.
- ^ Murrin, John (2006). Liberty, Equality, Power: A History of the American People. Belmont: Clark Baxter. p. 464. ISBN 978-0-495-91588-1
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 254–256.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 254.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 251–252.
- ^ Mansch 2005, p. 61.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 256.
- ^ White 2009, p. 350.
- ^ Nevins 1947, p. 4:312.
- ^ "Affairs of the Nation / The Change of Administration To-Day". The New York Times. March 4, 1861. p. 1.
- ^ Edgar 1998, p. 350.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 267; Potter 1977.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 267.
- ^ White 2009, p. 362.
- ^ Potter 1977, pp. 520, 569–570.
- ^ White 2009, p. 369.
- ^ White 2009, pp. 360–361.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 268.
- ^ Vorenberg 2001, p. 22; Vile 2003, pp. 280–281.
- ^ Lupton 2006, p. 34.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 273–277.
- ^ "Broadside, "President Lincoln's Farewell Address to His Old Neighbors, Springfield, February 12, 1861" - The Henry Ford". www.thehenryford.org . Retrieved December 5, 2020.
- ^ "Lincoln's Farewell Address – Illinois History & Lincoln Collections". Retrieved December 5, 2020.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 277–279.
- ^ Sandburg 2002, p. 212.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 283–284.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 268, 279.
- ^ Nevins 1959, p. 5:29.
- ^ Sherman 1990, pp. 185–186.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 293.
- ^ Oates 1974, p. 226.
- ^ Heidler, Heidler & Coles 2002, p. 174.
- ^ Harris 2011, pp. 59–71.
- ^ Neely Jr. 1992, pp. 3–31.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 303–304; Carwardine 2003, pp. 163–164.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 315–339, 417.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 314; Carwardine 2003, p. 178.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 314–317.
- ^ Carwardine 2003, p. 181.
- ^ Boritt & Pinsker 2002, pp. 213–214.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 322.
- ^ Randall, James Garfield (1946). Lincoln the President: Springfield to Gettysburg. p. 50. ISBN978-0-306-80754-1. quoted in Peraino, Kevin (2013) Lincoln in the World: The Making of a Statesman and the Dawn of American Power. pp. 160–61. ISBN 978-0-307-88720-7
- ^ Oates 1974, p. 115.
- ^ Thomas, Benjamin Platt; Hyman, Harold Melvin (1962). Stanton: The Life and Times of Lincoln's Secretary of War. Alfred A. Knopf. pp. 71, 87, 229–30, 385 (quote).
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 295–296.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 391–392.
- ^ Ambrose 1996, pp. 7, 66, 159.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 432–436.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 318–319.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 349–352.
- ^ "Henry W. Halleck". American Battlefield Trust. June 15, 2011. Archived from the original on October 8, 2018. Retrieved October 7, 2018.
- ^ Nevins 1947, pp. 159–162.
- ^ Nevins 1959, pp. 159–162.
- ^ Goodwin 2005, pp. 478–479.
- ^ Goodwin 2005, pp. 478–480.
- ^ Goodwin 2005, p. 481.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 389–390.
- ^ Nevins 1947, pp. 433–444; Donald 1996, pp. 429–431.
- ^ Nevins 1947, p. 322.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 422–423.
- ^ Nevins 1947, pp. 432–450.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 444–447.
- ^ Mackubin, Thomas Owens (March 25, 2004). "The Liberator". National Review. Archived from the original on February 16, 2012. Retrieved December 12, 2008.
- ^ Guelzo 1999, pp. 290–291.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 364–365.
- ^ McPherson 1992, p. 124.
- ^ Guelzo 2004, pp. 147–153.
- ^ Graebner 1959, p. 388.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 364, 379.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 407.
- ^ Louis P. Masur. (2012). Lincoln's Hundred Days: The Emancipation Proclamation and the War for the Union. Harvard University Press.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 430–431.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 431.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 408.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 453–460.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 460–466; Wills 2012, pp. 20, 27, 105, 146.
- ^ Bulla & Borchard 2010, p. 222.
- ^ Thomas 2008, p. 315.
- ^ Nevins 1947, pp. 4:6–17.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 490–492.
- ^ "Message of President Abraham Lincoln Nominating Ulysses S. Grant to Be Lieutenant General of the Army". National Archives. August 15, 2016.
- ^ McPherson 2009, p. 113.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 501.
- ^ "The Peacemakers". The White House Historical Association. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ Thomas 2008, pp. 422–424.
- ^ Neely Jr. 2004, pp. 434–458.
- ^ Thomas 2008, p. 434.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 565.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 589.
- ^ Fish 1902, pp. 53–69; Tegeder 1948, pp. 77–90.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 494–507.
- ^ Grimsley & Simpson 2001, p. 80.
- ^ Lincoln, Abraham (2001) [1953]. "Memorandum Concerning His Probable Failure of Re-election". Collected Works of Abraham Lincoln. Volume 7. p. 514.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 531.
- ^ Randall & Current 1955, p. 307.
- ^ Grimsley & Simpson 2001, p. 80; Paludan 1994, pp. 274–293.
- ^ Noll 2002, p. 426.
- ^ Lincoln, Abraham Abraham Lincoln: Selected Speeches and Writings (Library of America edition, 2009) p 450
- ^ Thomas 2008, pp. 509–512.
- ^ Koehn, Nancy (2017). Forged in Crisis: The Making of Five Legendary Leaders. NY: Scribner. p. 191. ISBN978-1-5011-7444-5.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 471–472.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 485–486.
- ^ Nevins 1947, p. 4:206.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 561.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 562–563; History.com.
- ^ "Primary Documents in American History: 13th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution". Library of Congress. Archived from the original on October 10, 2011. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ Carwardine 2003, pp. 242–243.
- ^ Lincove, David A. (2000). Reconstruction in the United States: An Annotated Bibliography. Greenwood. p. 80. ISBN978-0-313-29199-9.
- ^ Foner 2010, p. 335.
- ^ a b Nichols 1974, p. 3.
- ^ a b Nichols 1974, p. 4.
- ^ Bulla & Borchard 2010, p. 480.
- ^ Nichols 1974, pp. 4–5, 7.
- ^ a b Nichols 1974, p. 7.
- ^ Burlingame 2008, p. 481; Nichols 1974, p. 7.
- ^ a b Bulla & Borchard 2010, p. 481.
- ^ Nichols 1974, p. 8.
- ^ a b c Chomsky, Carol (1990). "The United States-Dakota War Trials: A Study in Military Injustice". Stanford Law Review. 43 (1): 13–98. doi:10.2307/1228993. ISSN 0038-9765. JSTOR 1228993.
- ^ Cox 2005, p. 182.
- ^ Bulla & Borchard 2010, p. 483.
- ^ Goodwin 2005, p. 319.
- ^ Goodwin 2005.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 137.
- ^ Paludan 1994, p. 116.
- ^ McPherson 2009, pp. 450–452.
- ^ Summers, Robert. "Abraham Lincoln". Internet Public Library 2 (IPL2). U. Michigan and Drexel U. Archived from the original on October 2, 2011. Retrieved December 9, 2012.
- ^ a b Donald 1996, p. 424.
- ^ Paludan 1994, p. 111.
- ^ Brands, H. W. (2011). Greenback Planet: How the Dollar Conquered the World and Threatened Civilization as We Know It. University of Texas Press. p. 1. ISBN978-0-292-73933-8.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 501–502.
- ^ a b c Donald 1996, p. 471.
- ^ Schaffer, Jeffrey P. (1999). Yosemite National Park: A Natural History Guide to Yosemite and Its Trails. Berkeley: Wilderness Press. p. 48. ISBN978-0-89997-244-2.
- ^ Blue 1987, p. 245.
- ^ "Biographical Directory of Federal Judges". Federal Judicial Center. Archived from the original on July 30, 2016. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- ^ "Federal judges nominated by Abraham Lincoln". BallotPedia. Archived from the original on September 9, 2015. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 300, 539.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 586–587.
- ^ Harrison 2010, pp. 3–4.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 594–597.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 597; Martin 2010.
- ^ Steers Jr. 2010, p. 153.
- ^ Fox, Richard (2015). Lincoln's Body: A Cultural History. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN978-0-393-24724-4.
- ^ Abel, E. Lawrence (2015). A Finger in Lincoln's Brain: What Modern Science Reveals about Lincoln, His Assassination, and Its Aftermath. ABC-CLIO. Chapter 14. ISBN978-1-4408-3118-8.
- ^ "OUR GREAT LOSS; The Assassination of President Lincoln". The New York Times. April 17, 1865. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on January 13, 2018. Retrieved April 12, 2016.
- ^ Hay, John (1915). The Life and Letters of John Hay Volume 1. Houghton Mifflin Company. Archived from the original on August 9, 2016. Retrieved July 9, 2018. Quote's original source is Hay's diary which is quoted in "Abraham Lincoln: A History", Volume 10, Page 292 by John G. Nicolay and John Hay
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 598–599, 686.
- ^ Hoch, Bradley R. (September 4, 2001). The Lincoln Trail in Pennsylvania: A History and Guide. Penn State Press. pp. 121–123. ISBN978-0-271-07222-7.
- ^ Trefousse, Hans L. (1989). Andrew Johnson: A Biography. W.W. Norton & Company. p. 194.
- ^ Steers Jr. 2010, p. 153; Donald 1996, p. 599.
- ^ Trostel 2002, pp. 31–58.
- ^ Trostel 2002, pp. 31–58; Goodrich 2005, pp. 231–238.
- ^ Peck, Garrett (2015). Walt Whitman in Washington, D.C.: The Civil War and America's Great Poet. Charleston, SC: The History Press. pp. 118–23. ISBN978-1-62619-973-6.
- ^ Hodes 2015, p. 164.
- ^ Hodes 2015, pp. 197–199.
- ^ Hodes 2015, pp. 84, 86, 96–97.
- ^ "Survey of Historic Sites and Buildings - Lincoln Tomb, Illinois". National Park Service. Archived from the original on August 30, 2009.
- ^ Carwardine 2003, p. 4; Wilson 1999, p. 84.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 48–49, 514–515.
- ^ Lincoln, Abraham (2001) [1953]. "Handbill Replying to Charges of Infidelity". Collected Works of Abraham Lincoln. Volume 1. p. 383.
- ^ a b Noll 1992.
- ^ "Religious Quotations by Abraham Lincoln". www.abrahamlincolnonline.org . Retrieved March 14, 2020.
- ^ Donald 1996, pp. 48–49.
- ^ Parrillo 2000, pp. 227–253.
- ^ White 2009, p. 180.
- ^ Brodrecht, Grant R. (2008). "Our Country": Northern Evangelicals and the Union During the Civil War and Reconstruction. University of Notre Dame.
- ^ Wilson 1999, pp. 251–254.
- ^ Wilson 1999, p. 254.
- ^ "Letter by Abraham Lincoln to Albert Hodges". www.abrahamlincolnonline.org . Retrieved March 14, 2020.
- ^ Wills, Garry (September 1, 1999). "Lincoln's Greatest Speech". The Atlantic . Retrieved March 14, 2020.
- ^ Lincoln, Abraham (2001) [1953]. Collected Works of Abraham Lincoln. Volume 8.
- ^ "Inaugural Addresses of the Presidents of the United States : from George Washington 1789 to George Bush 1989". avalon.law.yale.edu . Retrieved March 14, 2020.
- ^ Carwardine 2003, pp. 27–55.
- ^ Guelzo 1999, p. 434.
- ^ "What Can Lincoln's DNA Tell Us?". February 13, 2009. Retrieved February 20, 2020.
- ^ Hirschhorn, Norbert; Feldman, Robert G.; Greaves, Ian (Summer 2001). "Abraham Lincoln's Blue Pills: Did Our 16th President Suffer from Mercury Poisoning?". Perspectives in Biology and Medicine. Johns Hopkins University Press. 44 (3): 315–322. doi:10.1353/pbm.2001.0048. PMID 11482002. S2CID 37918186. Retrieved September 10, 2021.
- ^ Sotos, John G. (2008). The Physical Lincoln Sourcebook. Mt. Vernon Book Systems. ISBN978-0-9818193-3-4. Full-text index [1] [ permanent dead link ] paragraphs 612-626.
- ^ Mayell, Hillary (July 17, 2001). "Did Mercury in 'Little Blue Pills' Make Abraham Lincoln Erratic?". National Geographic News. Retrieved October 12, 2009.
- ^ a b Verghese, Abraham (May 20, 2009). "Was Lincoln Dying Before He Was Shot?". The Atlantic. Palo Alto, California. Archived from the original on April 13, 2014. Retrieved October 8, 2014.
- ^ Thomas 2008, p. 61.
- ^ Jaffa 2000, p. 399; Thomas 2008, p. 61.
- ^ Diggins 1986, p. 307; Thomas 2008, p. 61.
- ^ Foner 2010, p. 215; Thomas 2008, p. 61.
- ^ Jaffa 2000, p. 263; Thomas 2008, p. 61.
- ^ Burton, Orville Vernon (2008). The Age of Lincoln: A History. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN978-1-4299-3955-3.
- ^ Boritt & Pinsker 2002, pp. 196–198, 229–231, 301.
- ^ Harris 2007, p. 2.
- ^ Randall 1962, p. 175.
- ^ Belz 1998, p. 86.
- ^ Burt, Andrew (May 13, 2013). "'These United States': How Obama's Vocal Tic Reveals a Polarized America". The Atlantic . Retrieved February 14, 2020.
- ^ Douglass 2008, pp. 259–260.
- ^ Lindgren, James (November 16, 2000). "Rating the Presidents of the United States, 1789–2000". The Federalist Society . Retrieved February 14, 2020.
- ^ Densen, John V., ed. (2001). Reassessing The Presidency, The Rise of the Executive State and the Decline of Freedom. Auburn, Alabama: Ludwig von Mises Institute. pp. ix, 1–32. ISBN978-0-945466-29-1.
- ^ Newport, Frank (February 28, 2011). "Americans Say Reagan Is the Greatest U.S. President". Gallup.com. Archived from the original on March 14, 2012. Retrieved February 13, 2019.
- ^ Taranto & Leo 2004, p. 264.
- ^ Chesebrough 1994, pp. 76, 79, 106, 110.
- ^ Fornieri, Joseph R.; Gabbard, Sara Vaughn (2008). Lincoln's America: 1809–1865. Carbondale, Illinois: SIU Press. p. 19. ISBN978-0-8093-8713-7.
- ^ Randall 1962, pp. 65–87.
- ^ Schwartz 2000, p. 109.
- ^ Boritt & Pinsker 2002, p. 222.
- ^ a b Schwartz 2008, pp. 23, 91–98.
- ^ Schwartz 2008, pp. xi, 9, 24.
- ^ Schwartz 2008, pp. xi, 9.
- ^ Zilversmit, Arthur (1980). "Lincoln and the Problem of Race: A Decade of Interpretations". Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association. Springfield, Illinois: Abraham Lincoln Association. 2 (1): 22–24. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved December 2, 2018.
- ^ Barr, John M. (Winter 2014). "Holding Up a Flawed Mirror to the American Soul: Abraham Lincoln in the Writings of Lerone Bennett Jr". Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association. Springfield, Illinois: Abraham Lincoln Association. 35 (1): 43–65.
- ^ Bennett Jr. 1968, pp. 35–42.
- ^ Dirck 2008, p. 31.
- ^ Striner 2006, pp. 2–4.
- ^ Cashin 2002, p. 61; Kelley & Lewis 2005, p. 228.
- ^ Havers, Grant N. (November 13, 2009). Lincoln and the Politics of Christian Love. University of Missouri Press. p. 96. ISBN978-0-8262-1857-5.
- ^ Belz 2014, pp. 514–518; Graebner 1959, pp. 67–94; Smith 2010, pp. 43–45.
- ^ Carwardine, Richard; Sexton, Jay, eds. (2011). The Global Lincoln. Oxford, England: Oxford UP. pp. 7, 9–10, 54. ISBN978-0-19-537911-2.
- ^ Schwartz 2008, p. 146.
- ^ Donald 1996, p. 15.
- ^ Hirschkorn, Phil (January 17, 2009). "The Obama-Lincoln Parallel: A Closer Look". CBS News. New York City: CBS Corporation. Archived from the original on August 22, 2016. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- ^ Jackson, David (January 10, 2013). "Obama to be sworn in with Lincoln, King Bibles". USA Today. Mclean, Virginia. Archived from the original on March 24, 2015. Retrieved March 2, 2016.
- ^ Hornick, Ed (January 18, 2009). "For Obama, Lincoln was model president". CNN. Atlanta, Georgia: Turner Broadcasting Systems. Archived from the original on July 18, 2018. Retrieved August 5, 2018.
- ^ Spielberg, Steven; Kushner, Tony; Kearns Goodwin, Doris (2012). "Mr. Lincoln Goes to Hollywood". Smithsonian. Vol. 43 no. 7. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution. pp. 46–53.
- ^ Stokes, Melvyn (2011). "Abraham Lincoln and the Movies". American Nineteenth Century History. 12 (2): 203–231. doi:10.1080/14664658.2011.594651. S2CID 146375501.
- ^ Houseman, Donna; Kloetzel, James E.; Snee, Chad (October 2018). Scott Specialized Catalogue of United States Stamps & Covers 2019. Amos Media Company. ISBN978-0-89487-559-5.
- ^ Collea 2018, pp. 13–14.
- ^ Dennis 2018, p. 194.
- ^ Dennis 2018, p. 197.
- ^ "History of USS Abraham Lincoln (CVN 72)". United States Department of the Navy. Archived from the original on June 27, 2019. Retrieved February 13, 2020.
- ^ Pearson, Michael (February 16, 2016). "$18.5 million gift to help refurbish Lincoln Memorial". CNN. Retrieved February 13, 2020.
- ^ a b Nyce, Caroline Mimbs (May 21, 2015). "15 Most Visited National Landmarks in Washington, D.C." The Atlantic . Retrieved February 13, 2020.
- ^ "The Petersen House – Ford's Theatre". U.S. National Park Service . Retrieved February 13, 2020.
- ^ "Abraham Lincoln Historical Tours in Springfield, Illinois". lincolnlibraryandmuseum.com . Retrieved February 13, 2020.
- ^ "Mount Rushmore National Memorial". U.S. National Park Service. Archived from the original on October 1, 2011. Retrieved November 13, 2010.
Bibliography
- Ambrose, Stephen E. (1996). Halleck: Lincoln's Chief of Staff. Baton Rouge, Louisiana: LSU Press. ISBN978-0-8071-5539-4.
- Baker, Jean H. (1989). Mary Todd Lincoln: A Biography. New York, New York: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN978-0-393-30586-9.
- Bartelt, William E. (2008). There I Grew Up: Remembering Abraham Lincoln's Indiana Youth. Indianapolis, Indiana: Indiana Historical Society Press. ISBN978-0-87195-263-9.
- Belz, Herman (1998). Abraham Lincoln, constitutionalism, and equal rights in the Civil War era. New York, New York: Fordham University Press. ISBN978-0-8232-1768-7.
- Belz, Herman (2014). "Lincoln, Abraham". In Frohnen, Bruce; Beer, Jeremy; Nelson, Jeffrey O (eds.). American Conservatism: An Encyclopedia. Open Road Media. ISBN978-1-932236-43-9.
- Bennett Jr., Lerone (1968). "Was Abe Lincoln a White Supremacist?". Ebony. Vol. 23 no. 4. ISSN 0012-9011.
- Blue, Frederick J. (1987). Salmon P. Chase: A Life in Politics. Kent, Ohio: Kent State University Press. ISBN978-0-87338-340-0.
- Boritt, Gabor S.; Pinsker, Matthew (2002). "Abraham Lincoln". In Graff, Henry (ed.). The Presidents: A reference History (7th ed.). ISBN978-0-684-80551-1.
- Bulla, David W.; Borchard, Gregory A. (2010). Journalism in the Civil War Era. New York, New York: Peter Lang. ISBN978-1-4331-0722-1.
- Burlingame, Michael (2008). Abraham Lincoln: A Life. 2. Baltimore, Maryland: The Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN978-1-4214-1067-8.
- Carwardine, Richard J. (2003). Lincoln. London, England: Pearson Longman. ISBN978-0-582-03279-8.
- Cashin, Joan E. (2002). The War was You and Me: Civilians in the American Civil War. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN978-0-691-09174-7.
- Chesebrough, David B. (1994). No Sorrow Like Our Sorrow: Northern Protestant Ministers and the Assassination of Lincoln. Kent, Ohio: Kent State University Press. ISBN978-0-87338-491-9.
- Collea, Joseph D. Collea Jr. (September 20, 2018). New York and the Lincoln Specials: The President's Pre-Inaugural and Funeral Trains Cross the Empire State. McFarland. pp. 13–14. ISBN978-1-4766-3324-4.
- Cox, Hank H. (2005). Lincoln and the Sioux Uprising of 1862. Nashville, Tennessee: Cumberland House. ISBN978-1-58182-457-5.
- Dennis, Matthew (2018). Red, White, and Blue Letter Days: An American Calendar. Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press. ISBN978-1-5017-2370-4.
- Diggins, John P. (1986). The Lost Soul of American Politics: Virtue, Self-Interest, and the Foundations of Liberalism. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press. ISBN978-0-226-14877-9.
- Dirck, Brian R. (2008). Lincoln the Lawyer. Champaign, Illinois: University of Illinois Press. ISBN978-0-252-07614-5.
- Donald, David Herbert (1996). Lincoln. New York, New York: Simon and Schuster. ISBN978-0-684-82535-9.
- Douglass, Frederick (2008). The Life and Times of Frederick Douglass. New York, New York: Cosimo Classics. ISBN978-1-60520-399-7.
- Edgar, Walter B. (1998). South Carolina: A History. Columbia, South Carolina: University of South Carolina Press. ISBN978-1-57003-255-4.
- Ellenberg, Jordan (May 23, 2021). "What Honest Abe Learned from Geometry". Wall Street Journal. 278 (119): C3. Ellenberg's essay is adapted from his 2021 book, Shape: The Hidden Geometry of Information, Biology, Strategy, Democracy, and Everything Else, Penguin Press. ISBN 9781984879059
- Fish, Carl Russell (1902). "Lincoln and the Patronage". The American Historical Review. 8 (1): 53–69. doi:10.2307/1832574. JSTOR 1832574.
- Foner, Eric (2010). "The Fiery Trial: Abraham Lincoln and American Slavery". The SHAFR Guide Online. doi:10.1163/2468-1733_shafr_sim040100206.
- Goodrich, Th (2005). The Darkest Dawn: Lincoln, Booth, and the Great American Tragedy. Indianapolis, Indiana: Indiana University Press. ISBN978-0-253-34567-7.
- Goodwin, Doris Kearns (2005). Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham Lincoln. New York, New York: Simon and Schuster. ISBN978-0-684-82490-1.
- Graebner, Norman (1959). "Abraham Lincoln: Conservative Statesman". In Basler, Roy Prentice (ed.). The enduring Lincoln: Lincoln sesquicentennial lectures at the University of Illinois. Champaign, Illinois: University of Illinois Press. OCLC 428674.
- Grimsley, Mark; Simpson, Brooks D. (2001). The Collapse of the Confederacy. Lincoln, Nebraska: University of Nebraska Press. ISBN978-0-8032-2170-3.
- Guelzo, Allen C. (1999). Abraham Lincoln: Redeemer President. Grand Rapids, Michigan: Wm.B. Eerdmans Publishing Company. ISBN978-0-8028-3872-8.
- Guelzo, Allen C. (2004). Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation: The End of Slavery in America. New York, New York: Simon and Schuster. ISBN978-0-7432-2182-5.
- Harrison, J. Houston (1935). Settlers by the Long Grey Trail. Joseph K. Ruebush Co.
- Harrison, Lowell (2010). Lincoln of Kentucky. Lexington, Kentucky: University Press of Kentucky. ISBN978-0-8131-2940-2.
- Harris, William C. (2007). Lincoln's Rise to the Presidency. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas. ISBN978-0-7006-1520-9.
- Harris, William C. (2011). Lincoln and the Border States: Preserving the Union. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas.
- Heidler, David Stephen; Heidler, Jeanne T.; Coles, David J., eds. (2002). Encyclopedia of the American Civil War: A Political, Social, and Military History. New York, New York: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN978-0-393-04758-5.
- Heidler, David Stephen; Heidler, Jeanne T. (2006). The Mexican War. Santa Barbara, California: Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN978-0-313-32792-6.
- History.com, Editors. "House passes the 13th Amendment". History.com. Archived from the original on November 10, 2012. Retrieved May 4, 2020. CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- Hodes, Martha (2015). Mourning Lincoln. New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press. ISBN978-0-300-21356-0.
- Hofstadter, Richard (1938). "The Tariff Issue on the Eve of the Civil War". The American Historical Review. 44 (1): 50–55. doi:10.2307/1840850. JSTOR 1840850.
- Holzer, Harold (2004). Lincoln at Cooper Union: The Speech That Made Abraham Lincoln President. New York, New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN978-0-7432-9964-0.
- Jaffa, Harry V. (2000). A New Birth of Freedom: Abraham Lincoln and the Coming of the Civil War. Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN978-0-8476-9952-0.
- Kelley, Robin D. G.; Lewis, Earl (2005). To Make Our World Anew: Volume I: A History of African Americans to 1880. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press. ISBN978-0-19-804006-4.
- Lamb, Brian P.; Swain, Susan, eds. (2008). Abraham Lincoln: Great American Historians on Our Sixteenth President. New York, New York: PublicAffairs. ISBN978-1-58648-676-1.
- Lupton, John A. (2006). "Abraham Lincoln and the Corwin Amendment". Illinois Heritage. 9 (5): 34. Archived from the original on August 24, 2016.
- Luthin, Reinhard H. (1944). "Abraham Lincoln and the Tariff". The American Historical Review. 49 (4): 609–629. doi:10.2307/1850218. JSTOR 1850218.
- Madison, James H. (2014). Hoosiers: A New History of Indiana. Indianapolis, Indiana: Indiana University Press. ISBN978-0-253-01308-8.
- Mansch, Larry D. (2005). Abraham Lincoln, President-elect: The Four Critical Months from Election to Inauguration. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company. ISBN978-0-7864-2026-1.
- Martin, Paul (April 8, 2010). "Lincoln's Missing Bodyguard". Smithsonian Magazine. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved October 15, 2010.
- McGovern, George S. (2009). Abraham Lincoln: The American Presidents Series: The 16th President, 1861–1865. New York, New York: Henry Holt and Company. ISBN978-0-8050-8345-3.
- McPherson, James M. (1992). Abraham Lincoln and the Second American Revolution. New York, New York: Oxford University Press, USA. ISBN978-0-19-507606-6.
- McPherson, James M. (2009). Abraham Lincoln. New York, New York: Oxford University Press, USA. ISBN978-0-19-537452-0.
- Morse, John Torrey (1893). Abraham Lincoln. I. Cambridge, Mass., Riverside Press.
- Morse, John Torrey (1893). Abraham Lincoln. II. Cambridge, Mass. Riverside Press.
- Neely Jr., Mark E. (1992). The Fate of Liberty: Abraham Lincoln and Civil Liberties. New York, New York: Oxford University Press, USA. Archived from the original on October 29, 2014.
- Neely Jr., Mark E. (2004). "Was the Civil War a Total War?". Civil War History. 50 (4): 434–458. doi:10.1353/cwh.2004.0073.
- Nevins, Allan (1959). The War for the Union. New York, New York: Scribner. ISBN978-0-684-10416-4.
- Nevins, Allan (1947). The War for the Union and Ordeal of the Union, and the Emergence of Lincoln. New York, New York: Scribner.
- Nichols, David A. (1974). "The Other Civil War Lincoln and the Indians" (PDF). Minnesota History.
- Noll, Mark A. (1992). A History of Christianity in the United States and Canada. Grand Rapids, Michigan: Wm. B. Eerdmans. ISBN978-0-8028-0651-2.
- Noll, Mark A. (2002). America's God: From Jonathan Edwards to Abraham Lincoln. New York, New York: Oxford University Press, USA. ISBN978-0-19-515111-4.
- Oates, Stephen B. (1974). "Abraham Lincoln 1861–1865". In Woodward, Comer Vann (ed.). Responses of the Presidents to Charges of Misconduct. New York, New York: Dell Publishing. ISBN978-0-440-05923-3.
- Paludan, Phillip Shaw (1994). The Presidency of Abraham Lincoln. Lawrence, Kansas: University Press of Kansas. ISBN978-0-7006-0671-9.
- Parrillo, Nicholas (2000). "Lincoln's Calvinist Transformation: Emancipation and War". Civil War History. 46 (3): 227–253. doi:10.1353/cwh.2000.0073. ISSN 1533-6271.
- Potter, David M. (1977). The Impending Crisis: America Before the Civil War, 1848-1861. New York, New York: HarperCollins. ISBN978-0-06-131929-7.
- Randall, James Garfield (1962). Lincoln: The Liberal Statesman. New York, New York: Dodd, Mead & Co. ASIN B0051VUQXO.
- Randall, James Garfield; Current, Richard Nelson (1955). Lincoln the President: Last Full Measure. Lincoln the President. IV. New York, New York: Dodd, Mead & Co. OCLC 950556947.
- Richards, John T. (2015). Abraham Lincoln: The Lawyer-Statesman (Classic Reprint). London, England: Fb&c Limited. ISBN978-1-331-28158-0.
- Sandburg, Carl (1926). Abraham Lincoln: The Prairie Years. San Diego, California: Harcourt. OCLC 6579822.
- Sandburg, Carl (2002). Abraham Lincoln: The Prairie Years and the War Years. Boston, Massachusetts: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN978-0-15-602752-6.
- Schwartz, Barry (2000). Abraham Lincoln and the Forge of National Memory. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press. ISBN978-0-226-74197-0.
- Schwartz, Barry (2008). Abraham Lincoln in the Post-Heroic Era: History and Memory in Late Twentieth-Century America. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press. ISBN978-0-226-74188-8.
- Sherman, William T. (1990). Memoirs of General W.T. Sherman. Charleston, South Carolina: BiblioBazaar. ISBN978-1-174-63172-6.
- Simon, Paul (1990). Lincoln's Preparation for Greatness: The Legislative Years. Champaign, Illinois: University of Illinois Press. ISBN978-0-252-00203-8.
- Smith, Robert C. (2010). Conservatism and Racism, and Why in America They Are the Same. Albany, New York: State University of New York Press. ISBN978-1-4384-3233-5.
- Steers Jr., Edward (2010). The Lincoln Assassination Encyclopedia. New York, New York: HarperCollins. ISBN978-0-06-178775-1.
- Striner, Richard (2006). Father Abraham: Lincoln's Relentless Struggle to End Slavery. England, London: Oxford University Press. ISBN978-0-19-518306-1.
- Taranto, James; Leo, Leonard, eds. (2004). Presidential Leadership: Rating the Best and the Worst in the White House. New York, New York: Free Press. ISBN978-0-7432-5433-5.
- Tegeder, Vincent G. (1948). "Lincoln and the Territorial Patronage: The Ascendancy of the Radicals in the West". The Mississippi Valley Historical Review. 35 (1): 77–90. doi:10.2307/1895140. JSTOR 1895140.
- Thomas, Benjamin P. (2008). Abraham Lincoln: A Biography. Carbondale, Illinois: Southern Illinois University Press. ISBN978-0-8093-2887-1.
- Trostel, Scott D. (2002). The Lincoln Funeral Train: The Final Journey and National Funeral for Abraham Lincoln. Fletcher, Ohio: Cam-Tech Publishing. ISBN978-0-925436-21-4. Archived from the original on 2013.
- Vile, John R. (2003). "Lincoln, Abraham (1809–1865)". Encyclopedia of Constitutional Amendments: Proposed Amendments, and Amending Issues 1789–2002 (2nd ed.). ABC-CLIO. ISBN978-1-85109-428-8.
- Vorenberg, Michael (2001). Final Freedom: The Civil War, the Abolition of Slavery, and the Thirteenth Amendment. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. ISBN978-0-521-65267-4.
- Warren, Louis A. (2017). Lincoln's Youth: Indiana Years, Seven to Twenty-One, 1816-1830 (Classic Reprint). London, England: Fb&c Limited. ISBN978-0-282-90830-0.
- White, Ronald C. (2009). A. Lincoln: A Biography. New York, New York: Random House. ISBN978-1-58836-775-4.
- Wills, Garry (2012). Lincoln at Gettysburg: The Words that Remade America. New York, New York: Simon and Schuster. ISBN978-1-4391-2645-5.
- Wilson, Douglas Lawson; Davis, Rodney O.; Wilson, Terry; Herndon, William Henry; Weik, Jesse William (1998). Herndon's Informants: Letters, Interviews, and Statements about Abraham Lincoln. Univ of Illinois Press. pp. 35–36. ISBN978-0-252-02328-6.
- Wilson, Douglas L. (1999). Honor's Voice: The Transformation of Abraham Lincoln. New York: A. A. Knopf. ISBN978-0-307-76581-9.
- Winkle, Kenneth J. (2001). The Young Eagle: The Rise of Abraham Lincoln. Lanham, Maryland: Taylor Trade Publishing. ISBN978-1-4617-3436-9.
- Zarefsky, David (1993). Lincoln, Douglas, and Slavery: In the Crucible of Public Debate. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press. ISBN978-0-226-97876-5.
External links
Official
- Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library and Museum
- The Lincoln Presidential Library's ongoing digitization of all documents written by or to Abraham Lincoln during his lifetime
- Collected Works of Abraham Lincoln - complete collected works as edited by Basler et al (1958) - an online edition available through University of Michigan Library Digital Collections
- White House biography
Organizations
- Abraham Lincoln Association
- Abraham Lincoln Bicentennial Foundation
Media coverage
- "Abraham Lincoln collected news and commentary". The New York Times.
Other
- United States Congress. "Abraham Lincoln (id: L000313)". Biographical Directory of the United States Congress.
- Abraham Lincoln: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress
- "Life Portrait of Abraham Lincoln", from C-SPAN's American presidents: Life Portraits, June 28, 1999
- "Writings of Abraham Lincoln" from C-SPAN's American Writers: A Journey Through History
- Abraham Lincoln: Original Letters and Manuscripts – Shapell Manuscript Foundation
- Lincoln/Net: Abraham Lincoln Historical Digitization Project – Northern Illinois University Libraries
- Teaching Abraham Lincoln Archived December 10, 2017, at the Wayback Machine – National Endowment for the Humanities
- Works by Abraham Lincoln at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about Abraham Lincoln at Internet Archive
- Works by Abraham Lincoln at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)

- In Popular Song: Our Noble Chief Has Passed Away by Cooper/Thomas
- Abraham Lincoln Recollections and Newspaper Articles Collection Archived November 13, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, McLean County Museum of History
- Digitized items in the Alfred Whital Stern Collection of Lincolniana in the Rare Book and Special Collections Division in the Library of Congress
Where Is the Ford Theatre Where Lincoln Was Shot
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abraham_Lincoln